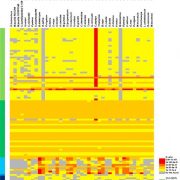
Viral sequences in the Arabidopsis genome ($) (Mol. Phylogenetics Evol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNumerous prokaryotic and eukaryotic genes have been identified as having homology to viral sequences. This phenomenon is the result of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) between viral pathogens and host cells. Chu and collaborators performed a proteome-wide analysis for the identification of viral domains…
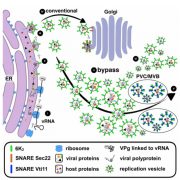
SNARE proteins in replication vesicle trafficking of turnip mosaic virus ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen plant cells are infected by RNA viruses, viral replication complexes are generated in organelle-like structures. These vesicles are important for the replication of viral RNA (vRNA) as well as moving vRNA-protein complexes through plasmodesmata to infect other plant cells. When turnip mosaic virus…
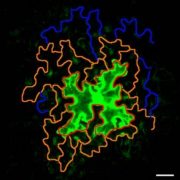
Arabidopsis Formin 2 regulates cell-to-cell trafficking through plasmodesmata (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlasmodesmata are cell-cell junctions that form cytosolic channels between neighboring plant cells. These junctions mediate the exchange of information between cells during various stress and developmental programs by actively regulating the aperture of the channel entrance or ‘pore’. In a new study…
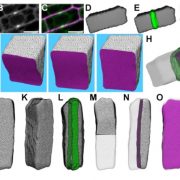
Predicting division planes of three-dimensional cells by soap-film minimization ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMartinez et al. used a modelling approach to see if it is possible to predict the location of a cell’s future division plane. In most cases the cell divides according to strict geometric rules, such that the newly formed wall will have a minimum area (described as a soap-film minimization model). However,…
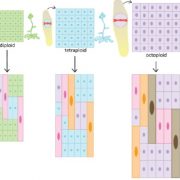
Ploidy and size at multiple scales in the Arabidopsis sepal (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPloidy refers to the number of genomes contained within a nucleus. Ploidy levels can increase through whole-genome duplication, which affects every cell equally, and through endoreduplication, a cell-by-cell process in which DNA synthesis is not accompanied by cytokinesis. Robinson et al. investigated…
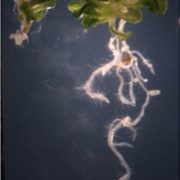
Epidermal expression of a sterol biosynthesis gene regulates root growth by a non-cell-autonomous mechanism in Arabidopsis (Development)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe HYDRA1 (HYD1) gene is primarily expressed in the root epidermis and encodes a sterol Δ8-Δ7 isomerase. The hyd1 mutant has defects in growth and radial patterning of root development. Short et al. showed that although HYD1 is not expressed in the vascular cells, PIN1 localization and vascular patterning…
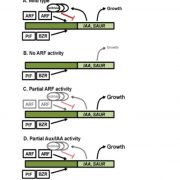
Three auxin response factors promote hypocotyl elongation (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBy now we’re probably all familiar with the central dogma of auxin signalling; that the interaction between auxin and auxin receptors (e.g., TIR1) leads to degradation of Aux/IAA proteins, freeing up ARF transcription factors to do their things. The complexity of this simple system arises in part due…

LTPs participate in preinvasive defense against powdery mildew pathogens (Mol. Plant Pathol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) display a strikingly clear capacity to bind lipidic molecules yet their mechanistic role in plant developmental or stress physiology is not yet clear. In a recent study published in Molecular Plant Pathology, Fahlberg et al. (2018) investigated the role of glycophosphatidylinositiol-(GPI)-anchored…
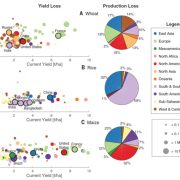
Increase in crop losses to insect pests in a warming climate ($) Science
Plant Science Research WeeklyMuch has been discussed about the impacts of abiotic effects (e.g., heat and drought stress) on crop yields arising from climate change. Here, Deutsch and Tewksbury et al. evaluate how a changing climate will affect crop (wheat, rice and maize) yields through increases in insect herbivory. Temperature…

