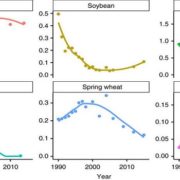
Long-term trends in the intensity and relative toxicity of herbicide use
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
“Weeds are a fact of life for farmers around the world,” writes Kniss in this analysis of herbicide-use trends. He stresses the limitation of reports that measure only the weight of herbicides used, as there is tremendous variation in the toxicity of different herbicides. He shows that although herbicide…
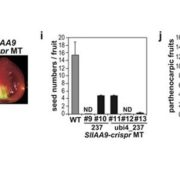
Rapid breeding of parthenocarpic tomato plants using CRISPR/Cas9
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchMost fruits form after pollination, making their production vulnerable to pollinator presence. Parthenocarpy is the development of fruit that occurs in the absence of pollination. Genes that enable parthenocarpy have been identified, including a tomato gene involved in auxin responses SlIAA9. Ueta et…
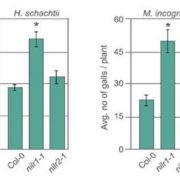
Arabidopsis leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase NILR1 is required for induction of innate immunity to parasitic nematodes
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPlant parasitic nematodes, including root-knot nematodes and cyst nematodes, cause extensive damage and loss to many crops. Nematodes elicit a pathogen-triggered immunity (PTI) defense response, but the molecular basis for this response has not been previously characterized. Mendy et al. identified a…
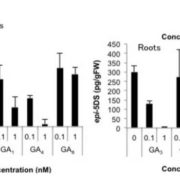
Regulation of strigolactone biosynthesis by gibberellin signaling
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchIn a screen for chemicals that regulate strigolactone (SL) levels in rice, Ito et al. found that gibberellins suppress SL biosynthesis. This effect depends on the gibberellin signaling module, and involve a decrease in expression level of SL-biosynthetic genes. Furthermore, GA treated rice exuded less…

Mutation in sorghum LOW GERMINATION STIMULANT 1 alters strigolactones and causes Striga resistance
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchStrigolactones are both hormones that control shoot architecture and signals that promote interactions with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and promote germination of detrimental parasitic weeds such as Striga asiatica and Striga hermonthica. Gobena et al. mapped and cloned a sorghum gene, LOW GERMINATION…
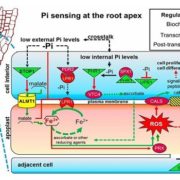
Malate-dependent Fe accumulation is a critical checkpoint in the root developmental response to low phosphate
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchPhosphate is a limiting nutrient in soil and not very mobile, so roots respond strongly to low Pi soils by the cessation of elongation of the primary root with accompanying stimulation of lateral root and root hair production. Previously, the accumulation of iron (Fe3+) in the apoplast of root meristem…
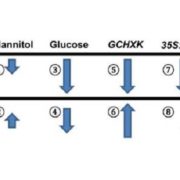
Sugar suppression of aquaporin expression and leaf hydraulics ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchSugar is a signal as well as an energy source, and plants monitor sugar levels to maintain an appropriate growth rate and rate of photosynthesis. A new study by Kelly et al. points to a role for sugars in the expression and activity of plasma-membrane (PIP) aquaporins. Aquaporins (AQP) are membrane channels…
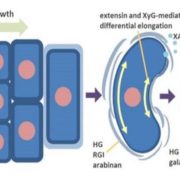
Pea border cell maturation and release involve complex cell wall structural dynamics
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchBorder cells form at the root tip and are shed during growth, protecting the sensitive root apex from damage as it pushes through the soil. Mravec et al. investigated the cell wall chemistry, carbohydrate distributioion and expression of cell-wall modifying genes to determine the mechanism by which border…

What We're Reading: April 21
Research, Research BlogReview: Rubisco activases: AAA+ chaperones adapted to enzyme repair
Rubisco, the fundamental enzyme required for photosynthetic carbon fixation, is susceptible to inactivation by the inhibitory binding of various metabolites. Rubisco activases (Rca’s) are enzymes that remodel Rubisco and facilitate…

