
Signatures of local adaptation in lowland and highland teosintes from whole genome sequencing of pooled samples ($)
0 Comments
/
Teosinte, the ancestor of maize, grows in a range of environments in México. Teosinte parviglumis (Zea mays ssp parviglumis) is more prevalent in lowland regions while teosinte mexicana (Zea mays ssp mexicana) occupies highland territory (>2000 m above sea level). Admixture between parviglumis and…
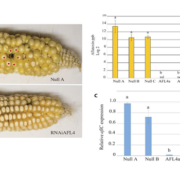
Aflatoxin-free transgenic maize using host-induced gene silencing
Aflatoxins are toxic metabolites produced by some species of Aspergillus fungi that can occur on numerous crop plants. When ingested by animals, aflatoxins cause health problems including liver cancer and stunted growth. Thakare et al. used host-induced gene silencing (HIGS) to block aflatoxin production…
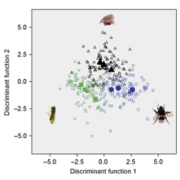
Divergent evolution driven by pollinators
A great variety of plants rely on pollinators to be fertilized successfully. This close relationship is thought to drive evolutionary diversification in plants, making the presence or absence of pollinators in response to climate change an increasingly relevant matter. Gervasi and Schiestl addressed…
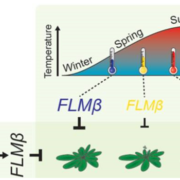
Natural haplotypes of FLM non-coding sequences fine-tune flowering time in two ambient spring temperatures in Arabidopsis
Delaying reproduction until conditions are favorable is a key to success. FLOWERING LOCUS C is a well-known regulator of flowering that delays flowering until after winter vernalization. In the spring, FLOWERING LOCUS M (FLM) fine-tunes flowering time in response to ambient temperatures between 5ºC…
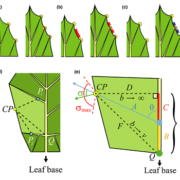
A common developmental program can produce diverse leaf shapes
The plethora of diverse leaf shapes results from variations of shared molecular mechanisms that govern leaf growth and development. To better understand the molecular underpinnings of diverse leaf morphologies, Runions et al. constructed a computational model of leaf development that included multiple…
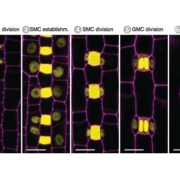
Mobile MUTE specifies subsidiary cells to build physiologically improved grass stomata ($)
Plants breathe through pores called stomata on leaf surfaces. Stomata are the point of contact with the outside world as they allow gas exchange (e.g., CO2 for photosynthesis) and transpiration. Grasses have evolved to form more efficient stomata in which the guard cells are flanked by additional subsidiary…

Root microbiota drive direct integration of phosphate stress and immunity
Many of the genes involved in the phosphate-stress response (PSR) have been identified from plants growing on sterile medium. Castrillo et al. examined how the root microbiota affectthe phosphate stress response, and how phosphate affects the association between roots and microbes. Plants deficient…
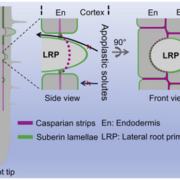
Role of LOTR1 in Nutrient Transport ($)
Casparian strips, named after the German botanist Robert Caspary who discovered them, are a cellular feature found in the roots of all higher plants. They are ring-like lignin polymers deposited in the middle of anticlinal cell walls (parallel to the root radius) between endodermal cells. Along with…
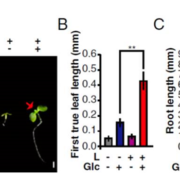
Differential TOR activation and cell proliferation in Arabidopsis root and shoot apexes
Growth and cell proliferation at the shoot and root apexes are regulated by diverse factors including hormones, nutrients, and light. Previously, the protein kinase TOR (Target of Rapamycin), a transducer of glucose energy signals, was shown to phosphorylate and activate the transcription factor E2Fa,…

