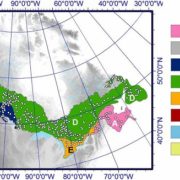
Growth-ring studies show no growth enrichment in Canadian boreal forests despite 50 years of CO2 enhancement
Plant Science Research Weekly, Research0 Comments
/
It has been argued that rising atmospheric CO2 levels might benefit plants by providing them more substrate for photosynthetic carbon-fixation. However, numerous studies have indicated that other factors interfere with a so-called CO2-fertilization benefit. Girardin et al. explore recent tree growth…
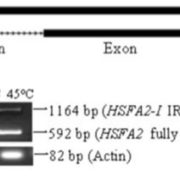
Integrating omics reveals insights into grape response to high temperature
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHeat stress is one of the main abiotic stresses plants encounter. Jiang et al. used combined transcriptomic and proteomic data to explore the responses of grape leaves to elevated temperatures (35, 40, 45°C). Using high-throughput sequencing and the iTRAQ (isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation)…

Genome sequence and genetic diversity of European ash trees
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAsh dieback (a fungal disease) and the beetle Agrilus planipennis (a herbivore) are crushing ash tree populations in the Northern Hemisphere. To shed light on the genetic basis of the trees' susceptibility and to understand the genetic diversity of these trees, Sollars et al. have sequenced one individual…
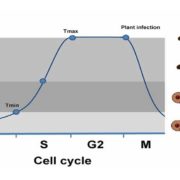
S-phase checkpoints regulate appressorium-mediated plant infection by rice blast fungus
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae causes a devastating disease of rice that can reduce harvests by 30%. Infection of plant tissues by the fungus requires the formation of an appressorium, a specialized structure that builds up sufficient pressure to burst through the plant cuticle. Previous work…

UV-B perceived by the UVR8 photoreceptor inhibits plant thermomorphogenesis
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchAmbient temperature can influence plant architecture, an effect termed thermomorphogenesis. In A. thaliana, thermomorphogenesis phenotypes include stem elongation and changes in leaf elevation angles. Increased auxin biosynthesis involving the transcription factor PIF4 is required for thermomorphogenesis,…

Homeodomain protein underpins leaf shape variation in cotton ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchHomeodomain transcription factors are well-known as regulators of developmental patterning, including in leaves. Andres et al. examine the molecular basis behind leaf shape in cotton, particularly the Okra locus that was identified by breeders as a regulator of leaf shape. They show that the Okra locus…

Review: The many roles of AVP1, a H+-PPase ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchThe AVP1 gene encodes a proton-pumping pyrophosphatase (H+-PPase) localized to the vacuolar membrane, which means that it pumps H+ into the vacuole using energy stored in pyrophosphatase (PPi). The direct consequences of its action are the acidification of the vacuole and the removal of PPi from the…
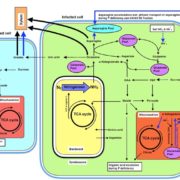
Review: Adaptive strategies for N metabolism in P deficient legume nodules ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchLegume nodules fix N, but their function has a high requirement for P, making nitrogen-fixation highly sensitive to P deficiency. Valentine et al. review how P limitation affects nodule function and also how nodules respond and adapt to P deficiency, drawing largely on studies of Virgilia divaricata,…

Review: Transport and homeostasis of K & P ($)
Plant Science Research Weekly, ResearchNitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are the three macronutrients required in highest amounts for plant growth. N is abundant in the atmosphere, therefore plentiful if we overlook the energetic costs of converting N2 to usable form. By contrast, K and P are present in limited amounts in the…

