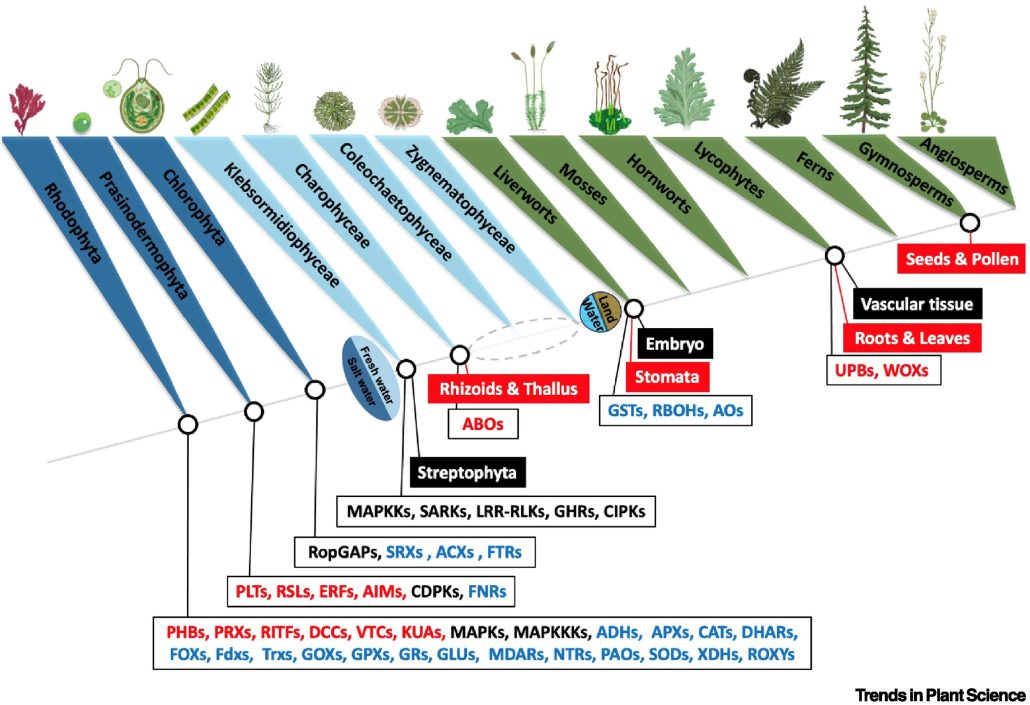
Review: Evolution of ROS targets for plant development
Plant Science Research WeeklyReactive oxygen species (ROS) are agents of damage but also potent signals. Here, Singh et al. review the cellular targets that support ROS signaling across the green kingdom. Many of the signaling roles for ROS have been uncovered in Arabidopsis and other angiosperms, so it is interesting to look at…

Tobacco leaf tissue rapidly detoxifies direct salt loads without activation of calcium and SOS signaling (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklySalinity stress is one of the primary abiotic causes of crop loss worldwide. In roots, the early response to high salt levels is coordinated largely via the well characterized salt-overly sensitive (SOS) pathway, which is dependent on Ca2+ signaling. However, how plants cope with elevated salt levels…
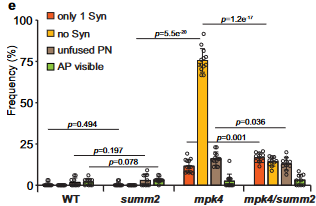
ROS homeostasis mediated by MPK4 and SUMM2 determines synergid cell death (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFemale gametophytes (FG) of angiosperms contain eight nuclei and seven cells, distributed in a defined manner. In the micropylar end of the FG there are two synergid cells and the haploid egg, while in the central cell there are two polar nuclei. The synergid cells are responsible for attracting the…

Reactive oxygen species homeostasis in rose petals
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellZhang et al. show that a transcription factor module modulates TCA cycle strength and thus reactive oxygen species homeostasis in rose petals. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koab152
Background: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are by-products of several primary metabolic pathways and high…

