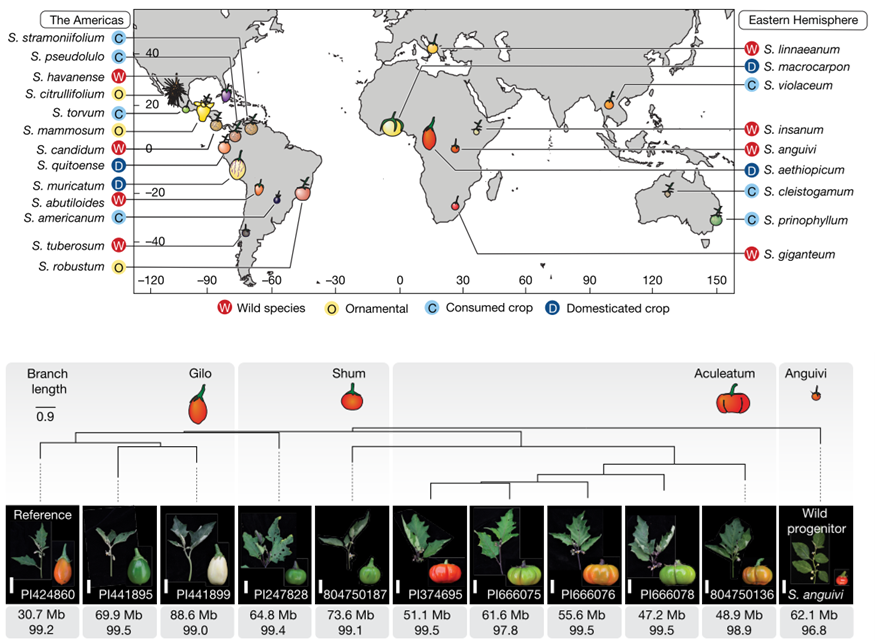
Double trouble: The Solanum pan-genome shows gene duplication complicates predictability
Plant Science Research WeeklyA pan-genome has been assembled for the Solanum genus, which contains many diverse and economically important crops including potato, tomato, and African eggplant. Genomes were assembled for 22 species, and genes were predicted based on previous reference genomes and from RNA sequences across multiple…
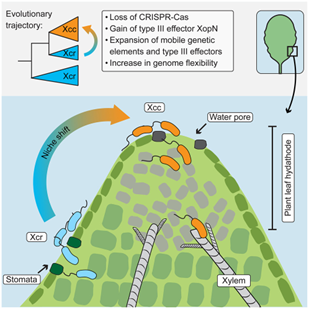
Shaping pathogenicity: How CRISPR-Cas loss fuels Xanthomonas evolution
Plant Science Research WeeklyPathogens have evolved diverse infection strategies governed by virulence factors, often targeting specific host organs or tissues. Genome fluidity plays a crucial role in enabling microbial pathogens to adapt to the dynamic selection pressures imposed by co-evolution with their hosts. In a recent study,…
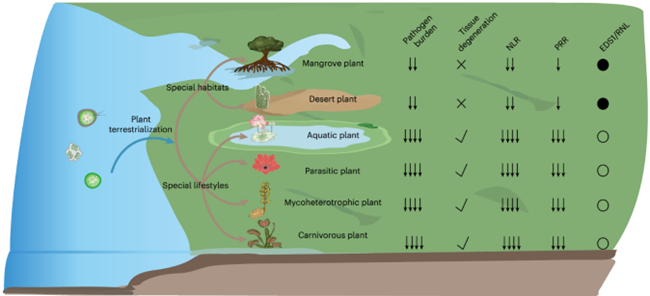
Streamlining the immune system: How plants adapt to reduced pathogen pressure
Plant Science Research WeeklyAlthough plants are sessile organisms unable to escape pathogen invasions, they are well equipped with defense mechanisms. Cell surface-localized pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) detect extracellular signals and initiate pattern-triggered immunity (PTI), while nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat…
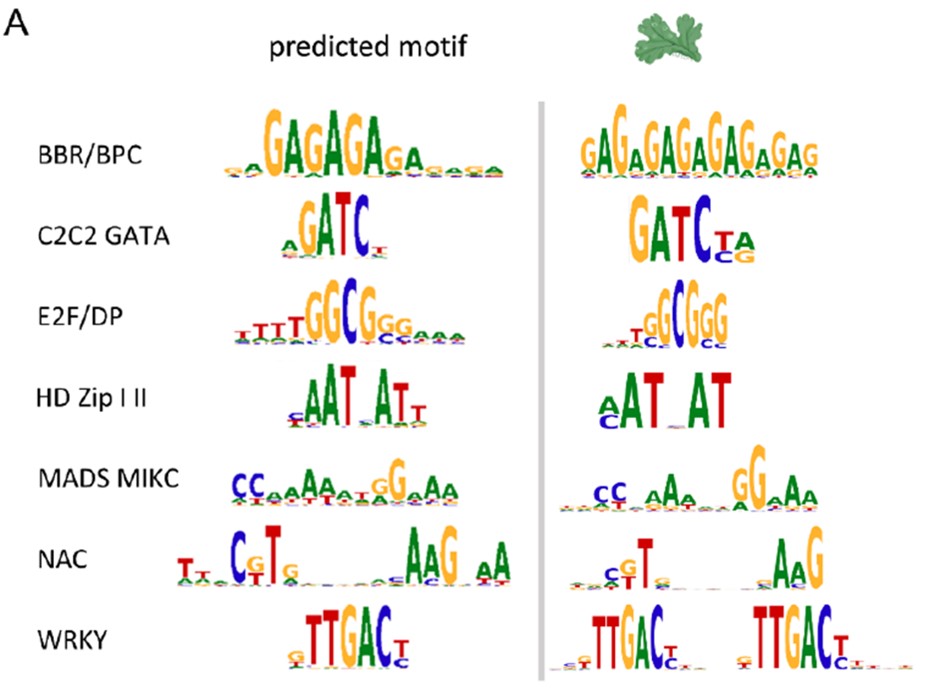
Many plant transcription factor families have evolutionarily conserved binding motifs
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe regulated expression of genes is fundamental to all biological processes, including development, cell growth, and responses to environmental signals. Transcription factors (TFs) are sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins that play a central role in transcriptional regulation by directly interacting…
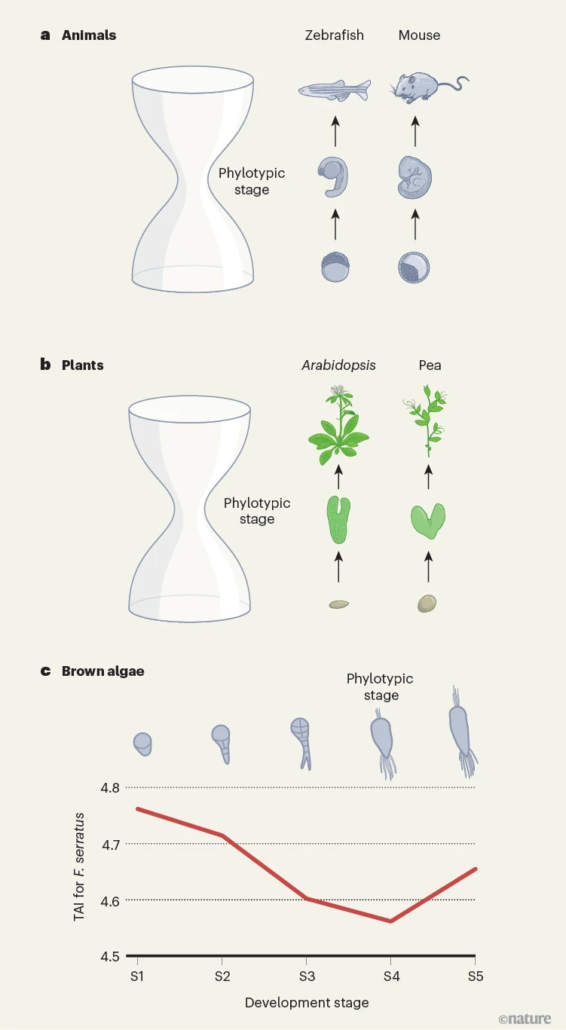
The ”hourglass” model of embryogenesis extends to brown algae
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe hourglass model of embryogenesis was proposed in the 1990s, and extended to green plants and fungi in the 2010s. During animal embryogenesis, the very earliest stages (post fertilization) are morphologically quite different from each other, and the later stages are quite different, but in the middle…

Convergent evolution of plant prickles
Plant Science Research WeeklyContrary to common belief, roses do not have thorns: instead, they have prickles. Thorns (as in hawthorns) are modified stems, spines (as in cactus spines) are modified leaves, and prickles (as in roses) are modified epidermal tissues. Prickles occur in a wide range of plants. Satterlee et al. set out…
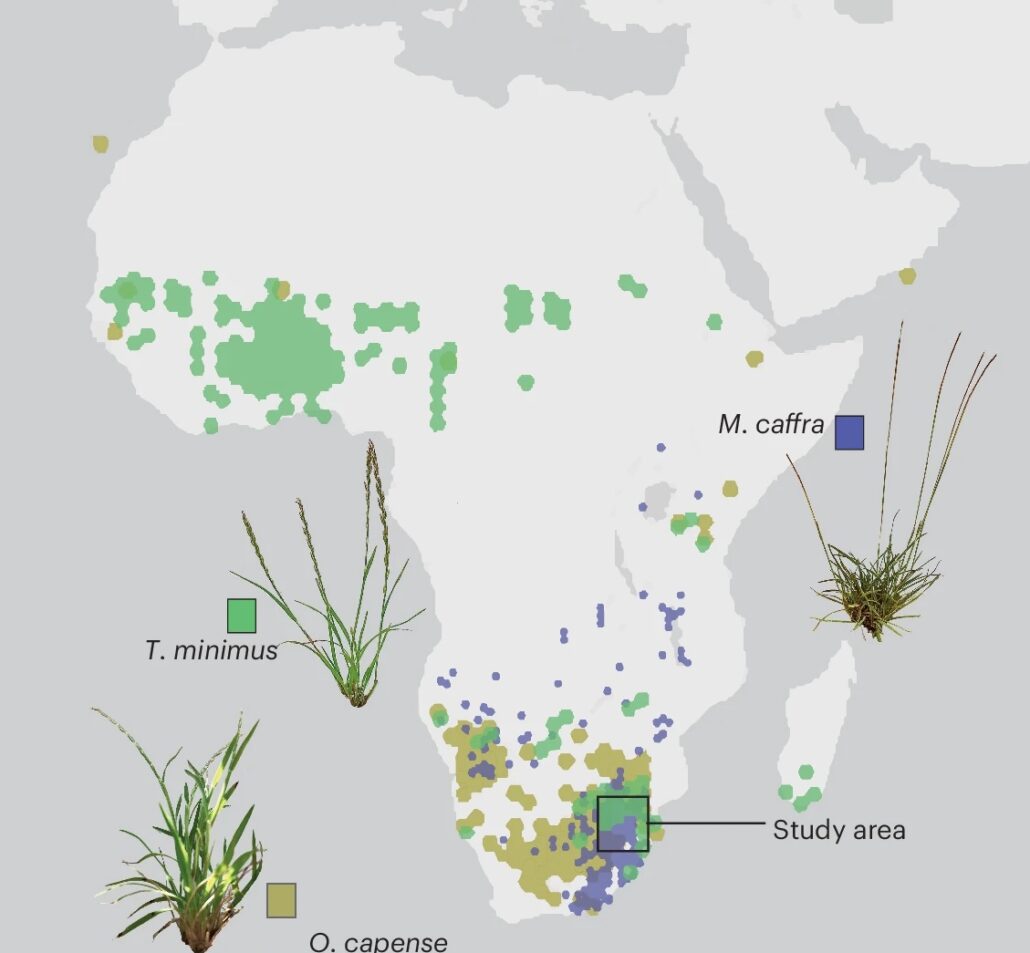
Convergent evolution of desiccation tolerance in grasses
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany bryophytes and other non-seed plants are tolerant to vegetative desiccation, which is thought to have been necessary for colonization of land. By contrast, most seed plants lack this capacity, although they retain desiccation tolerance in their pollen and seeds. However, some seed plants, known…
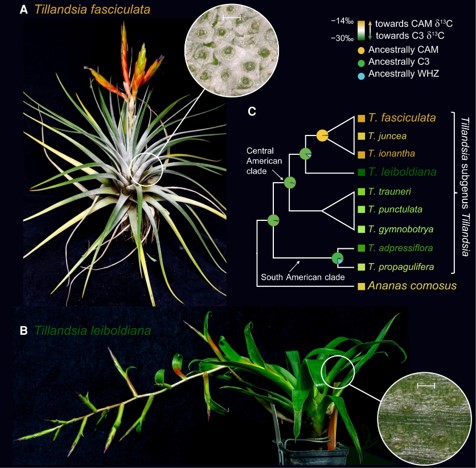
CAM evolution is associated with gene family expansion in an explosive bromeliad radiation
Plant Science Research WeeklyStudies on Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) plant genomes are scarse and CAM evolution is known to be an ecological driver of diversification. The subgenus Tillandsia (Bromeliaceae) is one of the fastest diversifying clades in the plant kingdom and is known for its adaptive CAM trait. It has recently…
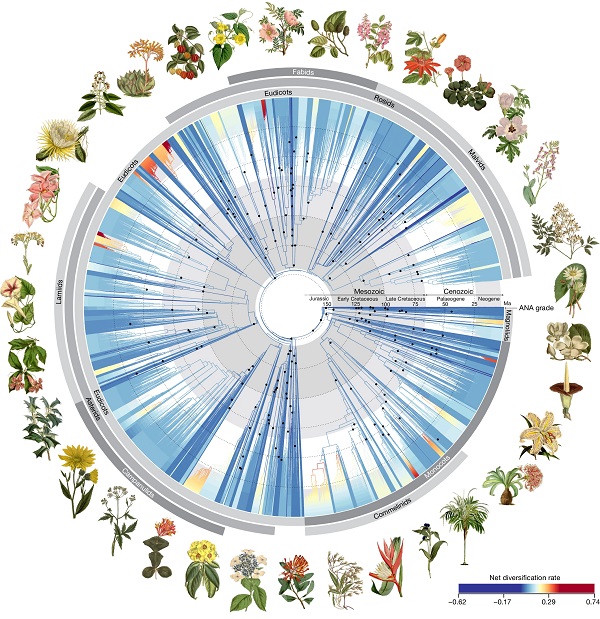
Phylogenomic insights into angiosperm evolution
Plant Science Research WeeklyLow-resolution data can provide broad strokes but miss the details that come from greater information density. When striving to understand the multimillion-year evolutionary history of the angiosperms, more data certainly helps. Here, by focusing on a subset of 353 genes, Zuntini and Carruthers et al.…

