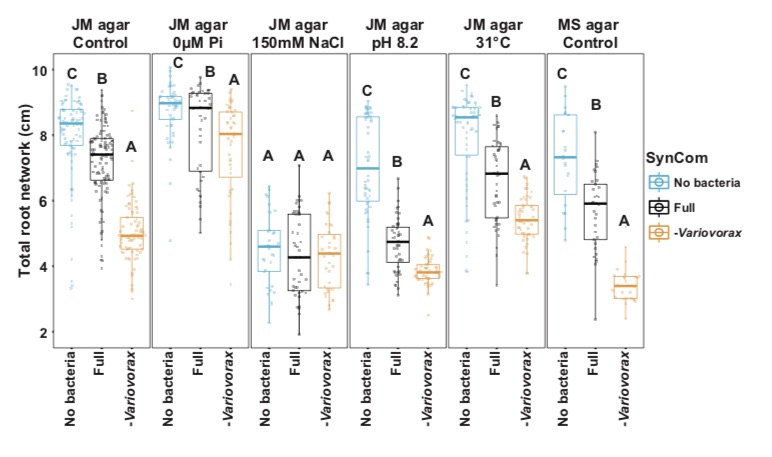
Root development is maintained by specific bacteria-bacteria interactions (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyUnderstanding plant-microbe and microbe-microbe interactions is challening. Both kinds of interactions have significant impacts on plant health and nutritional uptake. Finkel et al. address how microbe-microbe interactions shape plant phenotypes by using the synthetic microbial community (SynCom) consisting…

Functional traits and phenotypic plasticity modulate species coexistence across contrasting climatic conditions (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyUnderstanding mechanisms for assembly of plant communities involves estimating different interactions among coexisting species, and how environmental change might affect those interactions. Peréz-Ramos et al. address how functional traits and their plasticity relate to the mechanisms that allow species…

Drought conditions reduce root-feeding nematode predator populations (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyClimate change is expected to cause numerous negative impacts on plant populations. An under considered area that will be affected are the communities of soil organisms that rely on a delicate balance of environmental conditions, particularly in grasslands that receive moderate precipitation (mesic grasslands).…
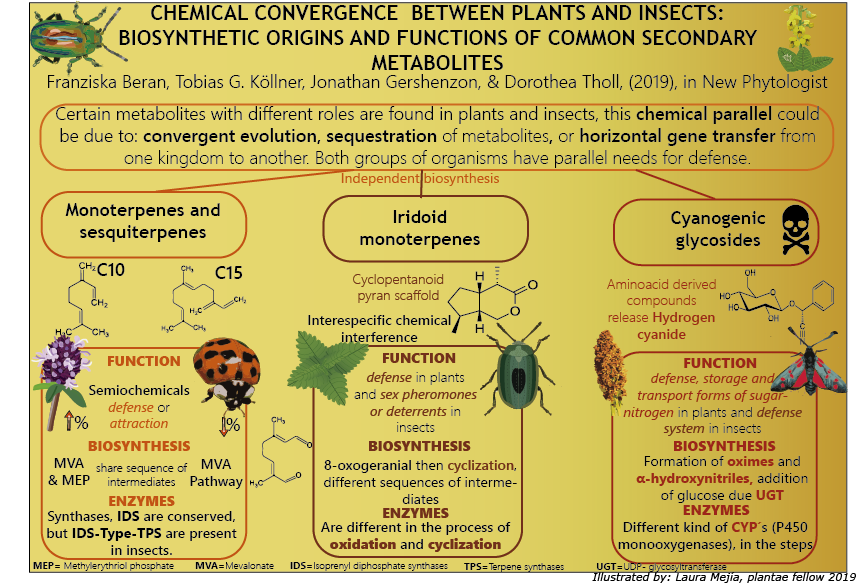
Review. Chemical convergence between plants and insects: biosynthetic origins and functions of common secondary metabolites (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research Weekly
Plants and insects aren't closely related, but they have a plethora of similar chemical weapons used for their interactions (defense, attraction, etc.). Beran et al. describe the function and biosynthesis of secondary metabolites that are shared in both insects and plants.
The monoterpenes and…
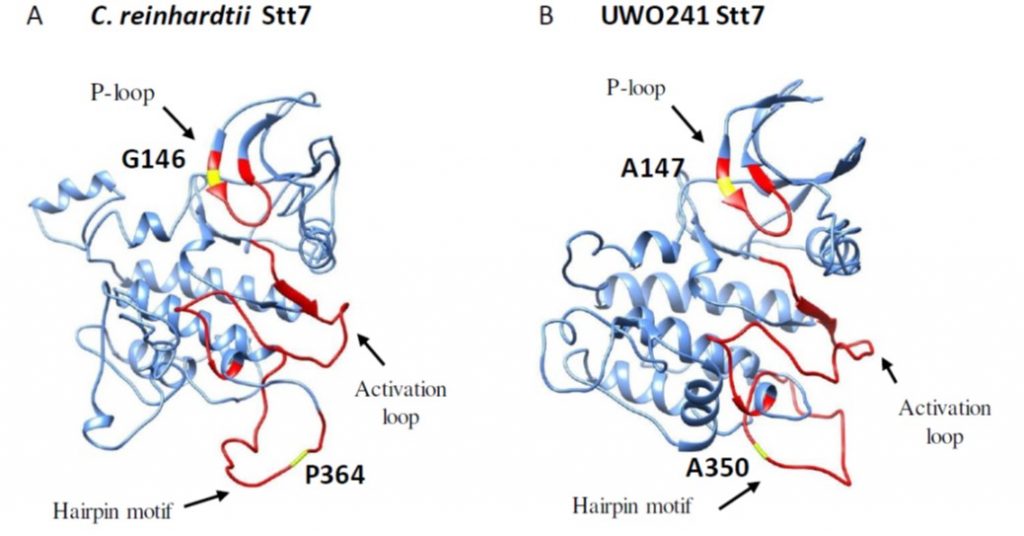
Cold-adapted protein kinases and thylakoid remodeling impact energy distribution in an Antarctic psychrophile (Plant Phys)
Plant Science Research Weekly“Earth is a cold place with 80% of its biosphere permanently below 5°C,” begins this study of an Antarctic psychrophile (“cold-lover”). As Szyszka-Mroz et al. indicate, the permanently cold-adapted inhabitants of permanently frozen lakes are highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change,…
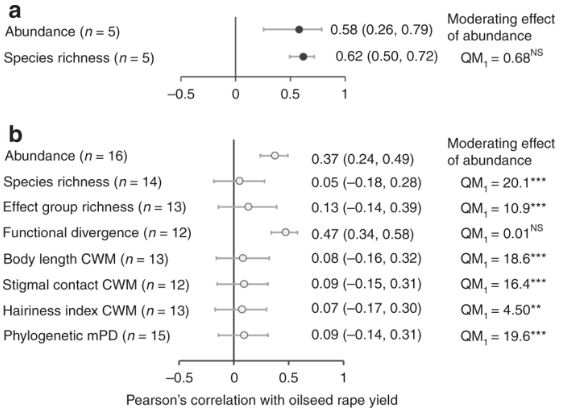
Pollinator functional diversity and abundance enhance crop pollination and yield (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyInsects provide a valuable service to the agricultural industry through pollination, which increases both the quality and harvest volume for many important food crops, however little is known regarding the role of insect functional trait differences in promoting crop pollination. Woodcock et al. tested…
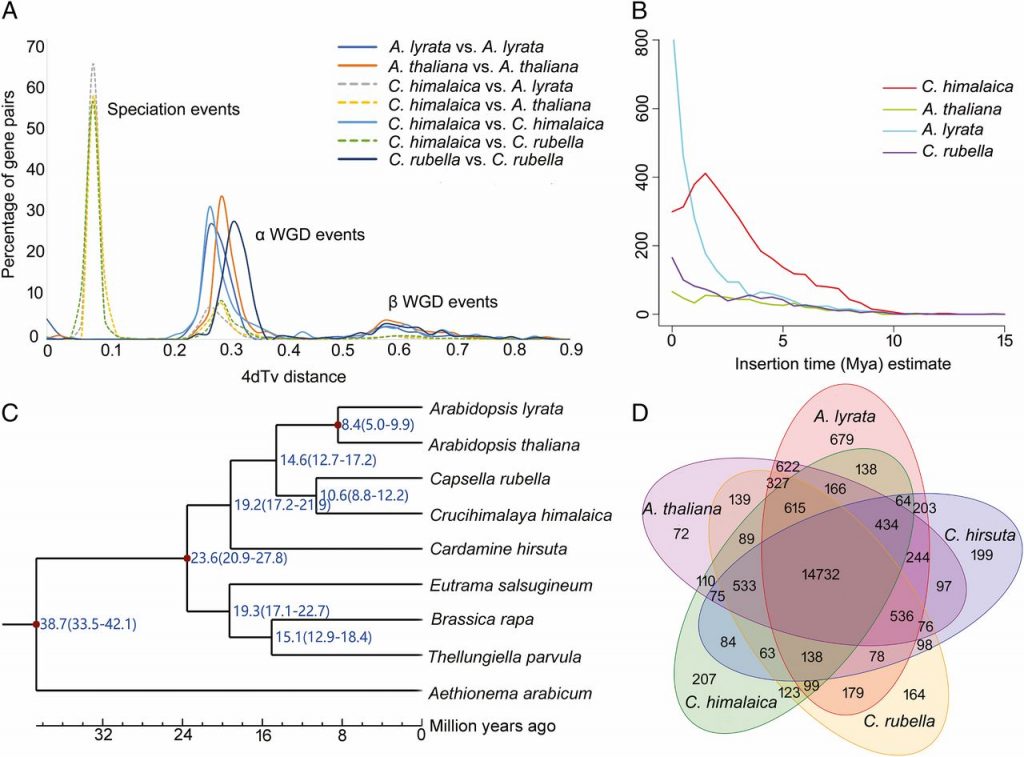
Dramatic changes in repeat element content and gene family sizes underlie the high-altitude adaptation of rock-cress (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe ability to grow on the ‘roof of the world’ - the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, makes Crucihimalaya himalaica (Rock-cress) an important model for studying adaptive evolution. A draft genome sequence of C. himalaica reported by Zhang et al. now provides clues to its speciation and ecological adaptation.…
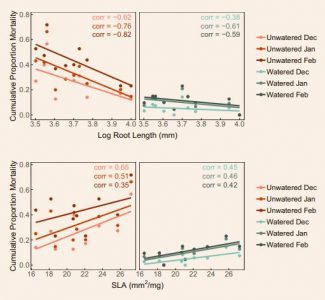
Seedling traits predict drought-induced mortality linked to diversity loss (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen trying to understand the repercussions climate change will have on future plant communities, trait-based approaches provide valuable insight. Unfortunately, many trait-based studies focus only on the above-ground traits of un-stressed adult plants, ignoring the critical seedling stage. Harrison…
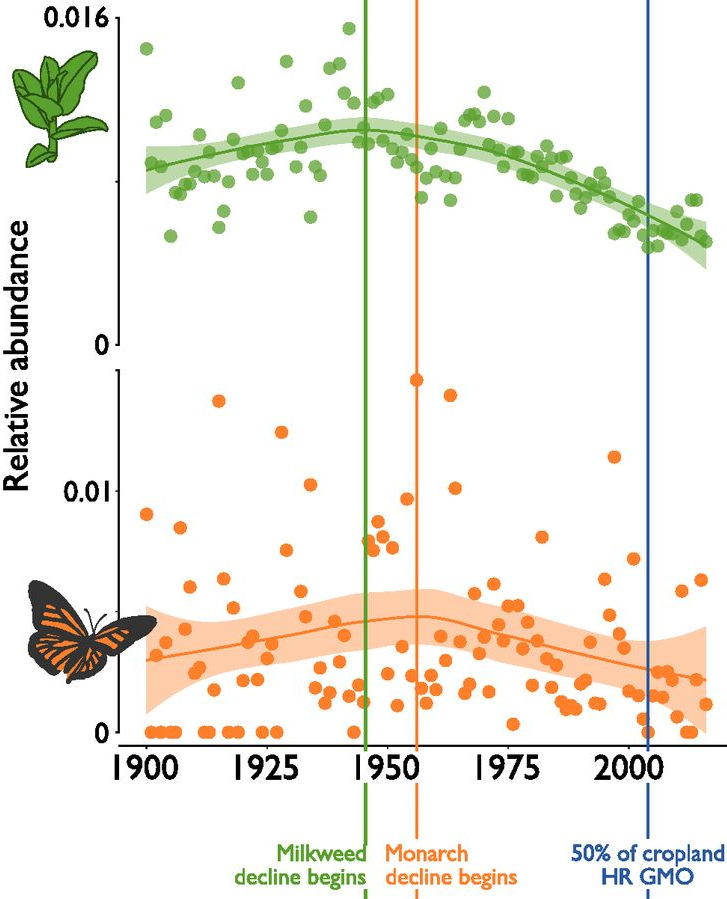
Century-old museum specimens predict a timeline for declines in monarch butterflies and their host milkweed (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMilkweeds are often found in agriculture fields, and are susceptible to herbicides sprayed in such fields. A decline in milkweeds, which provide food for monarch butterflies, has been historically linked to the wide cultivation of herbicide-resistant genetically modified (GM) crops. Boyle et al. attempt…

