
Review: Till death do us pair: Co-evolution of plant–necrotroph interactions
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis interesting and well-written review by Derbyshire and Raffaele takes a step back from the molecular interactions between plant and pathogen and discusses them in light of co-evolutionary processes. The review starts with a useful introduction and definition of concepts about “robustness” in…
Review: Challenges to improving plant growth through introduced microbes
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are closely associated with large numbers of microbes that live in, on, and around them; these are collectively called the plant microbiota. Microbes can be pathogenic, neutral, or beneficial. Beneficial microbes might enhance nutrient uptake by the plant or suppress pathogenic microbes. There…

Listening to the whispers in the air: Plant eavesdropping in action
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants release a variety of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including green leaf volatiles (GLVs), terpenoids, and amino acid derivatives, in response to herbivore damage and injury. Healthy neighboring plants detect these VOCs as warning signals, prompting them to activate defense mechanisms. This…

Many modes of Striga resistance in sorghum
Plant Science Research WeeklyWitchweeds (Striga spp.) are parasitic plants. Like other weeds, they compete with food crops, but they do so very efficiently by penetrating host tissues and forming vascular connections. Through this effective extraction of nutrients and photosynthate from their hosts, Striga can literally wipe out…

Review: Improving RNA-based crop protection through nanotechnology and insights from cross-kingdom RNA trafficking
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe German physician Paul Ehrlich (not to be confused with the American scientist of the same name) coined the term “magic bullet” (zauberkugel) to describe something that is perfectly and accurately effective. As much as we dream of magic bullets, they are rarely found, but the idea of using spray-on…
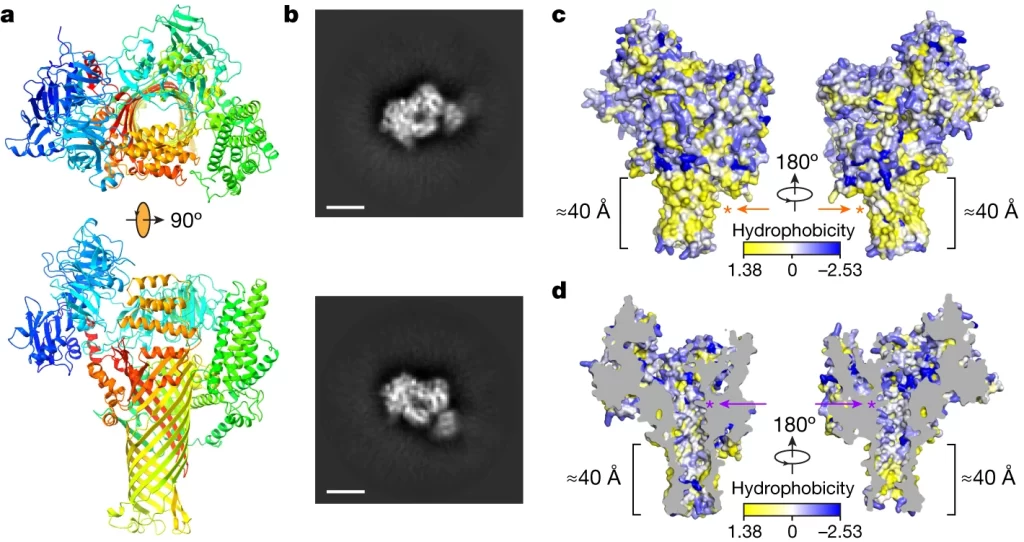
Bacterial pathogens deliver water- and solute-permeable channels to plant cells
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhat do you do when you’ve identified a gene that you know is important, but you don’t know how it functions? Usually, you can get hints from homology searches, overexpression studies, or the identification of protein domains, but sometimes those approaches don’t work. That’s where the story…
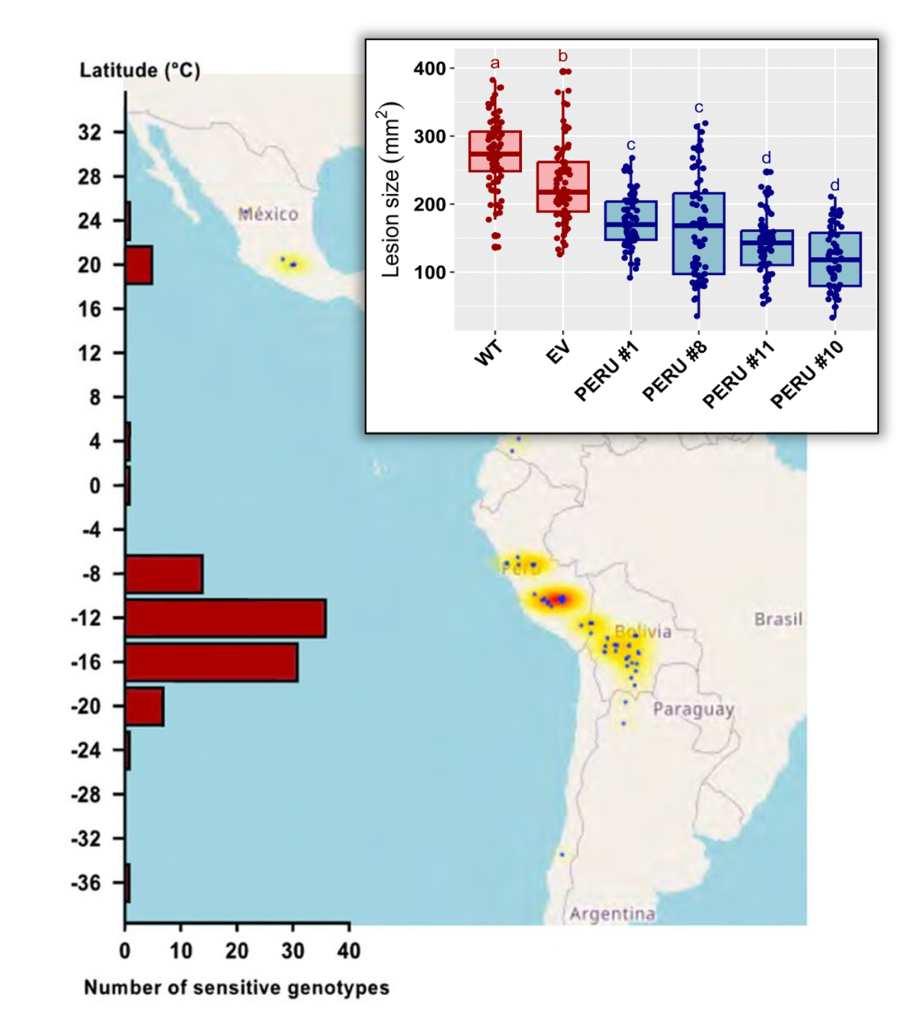
Functional diversification of a wild potato immune receptor at its center of origin
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn many biology textbook, plant pathology is introduced through the historical context of the 1840s great potato famine, caused by colonial ideologies and a virulent pathogen. This causal agent, Phytophthora infestans, is an oomycete that is still present in the environment and causing outbreaks of late…
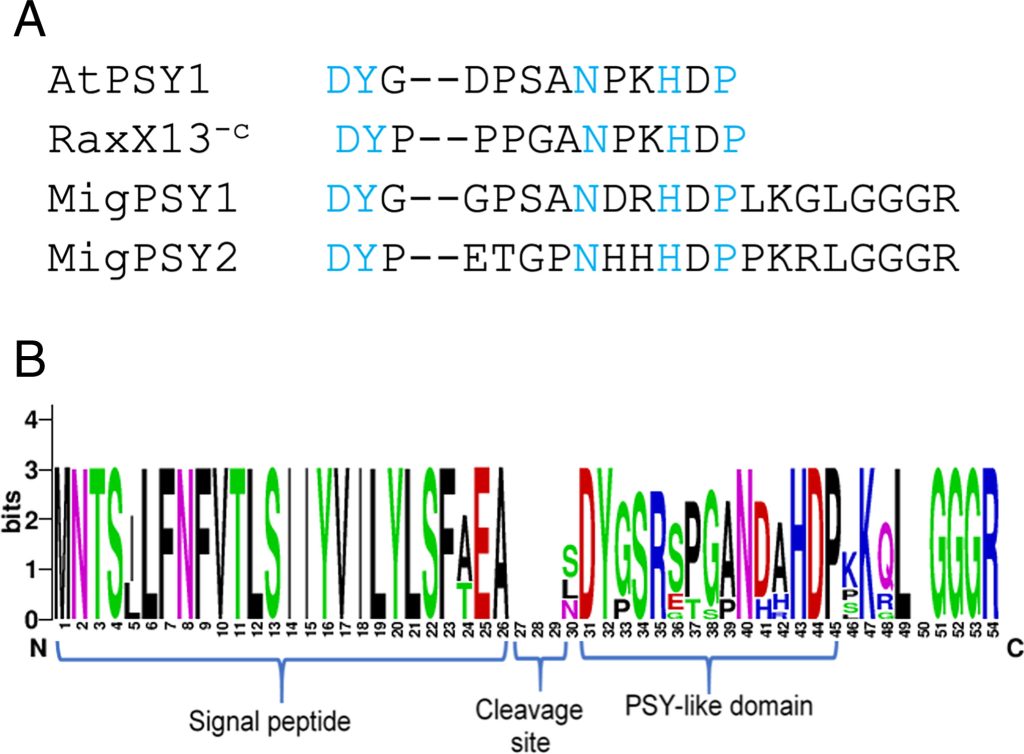
Root-knot nematodes produce functional mimics of tyrosine-sulfated plant peptides
Plant Science Research WeeklyI love reading about pathogens hijacking host systems; I’m always thrilled to see how “life finds a way”. Here’s another. Plants use a variety of peptides as hormones, many of which have covalent modifications of one sort or another. One class are the tyrosine-sulfated peptides, the PLANT PEPTIDE…

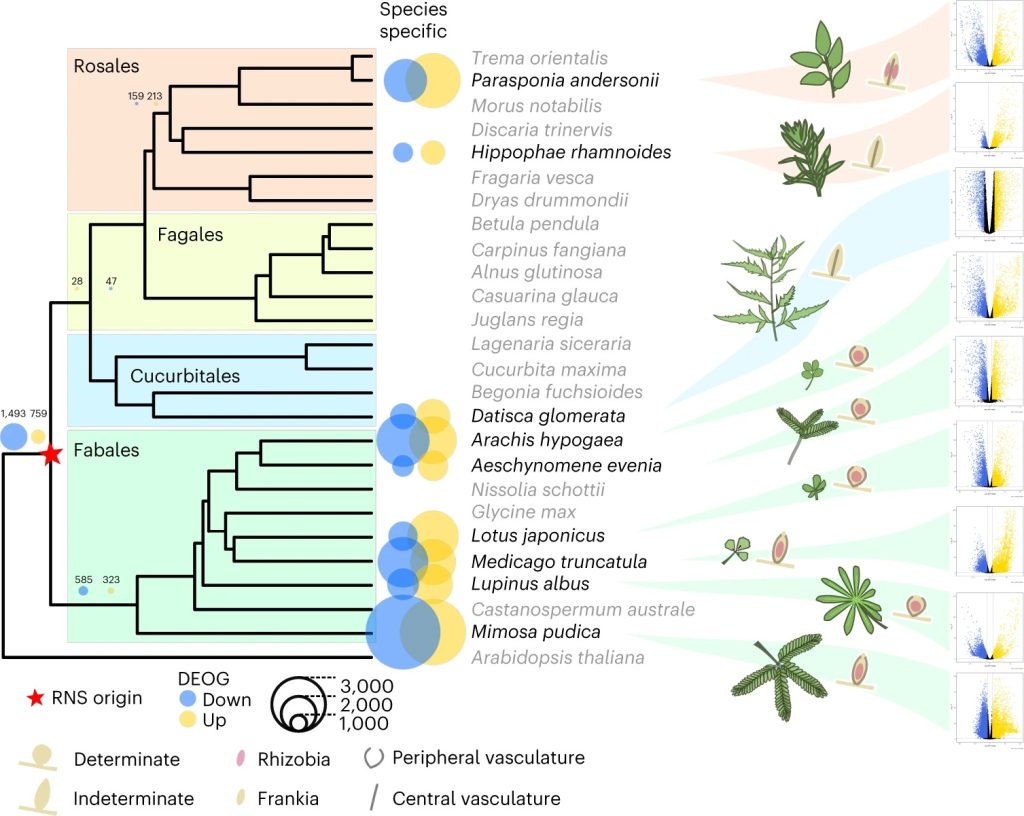
Comparative phylotranscriptomics reveals ancestral and derived root nodule symbiosis programs
Plant Science Research WeeklyThere are about ~17,500 plants species that can participate in nitrogen-fixing root nodule symbioses. The majority of these (~17,300) are in the order Fabales, which includes the legumes. The remainder fall into three orders (Rosales, Fagales, and Cucubitales), leading to the question of whether this…

