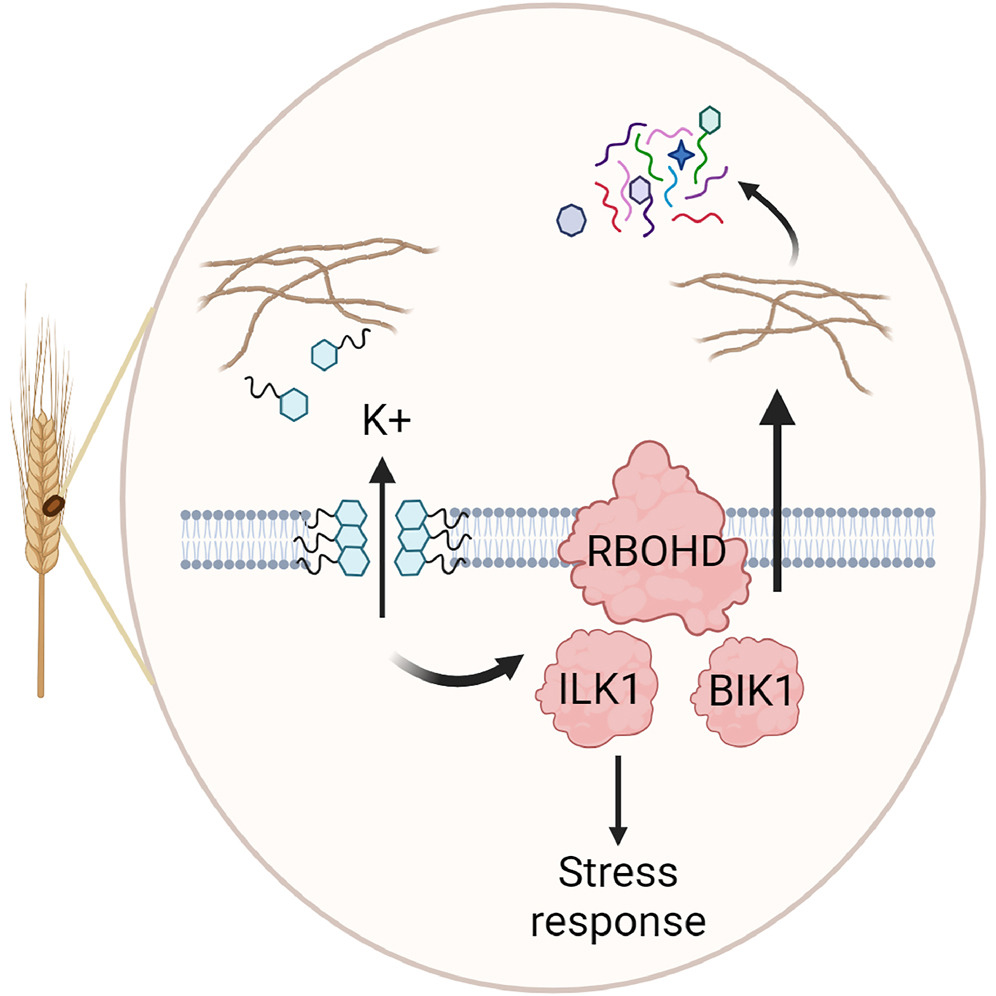
Pathogen cyclic lipopeptide virulence factors promote disease by inducing membrane leakage
Plant Science Research WeeklyPathogens deploy an array of molecules to create favorable conditions and promote infections in host plants. These molecules are well-known for suppressing host immunity, rendering them more susceptible. However, two recent reports suggest that some pathogen-produced virulence factors may also act independently…
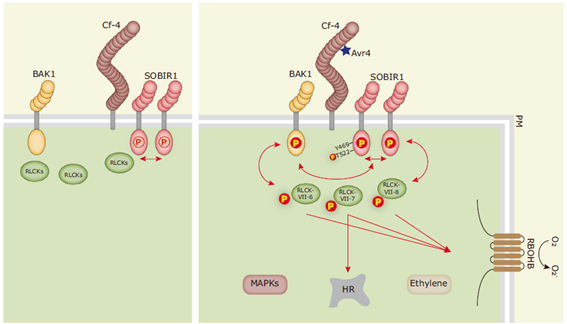
Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases of different subfamilies differentially regulate immune responses
Plant Science Research WeeklyCell surface receptor complexes act as the first line of defense in detecting pathogens and preventing invasion. Upon recognizing extracellular immunogenic patterns, a cascade of signaling relays occurs, mediated by phosphorylation events among a large array of membrane-associated proteins. These proteins…
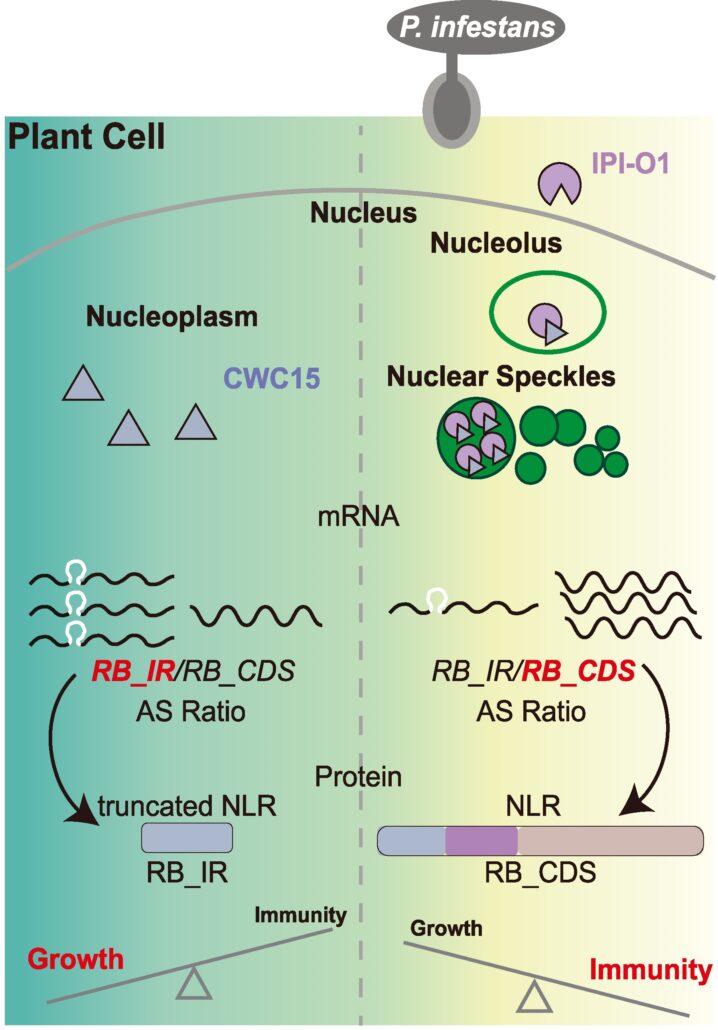
Alternative splicing of a disease resistance gene maintains homeostasis between growth and immunity
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant resistance genes encode proteins that trigger immune responses when they recognize pathogen effectors. Their activation must be carefully regulated, as overexpression of activation of R genes usually causes a decrease in growth rate. Here, Sun et al. investigated the role of alternative splicing…
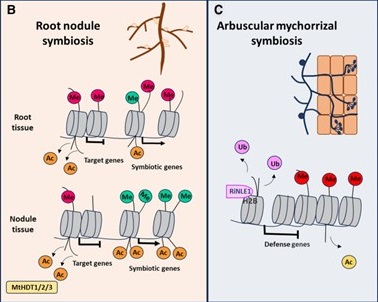
Review: Root development and symbiosis: an epigenetic perspective
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots do not grow in isolation but occupy a space inhabited by a variety of organisms. With certain fungi and bacteria, they form partnerships or symbiotic relationships that increase the plant’s nutrient uptake and assimilation. While the knowledge on the genetic programs required to establish these…
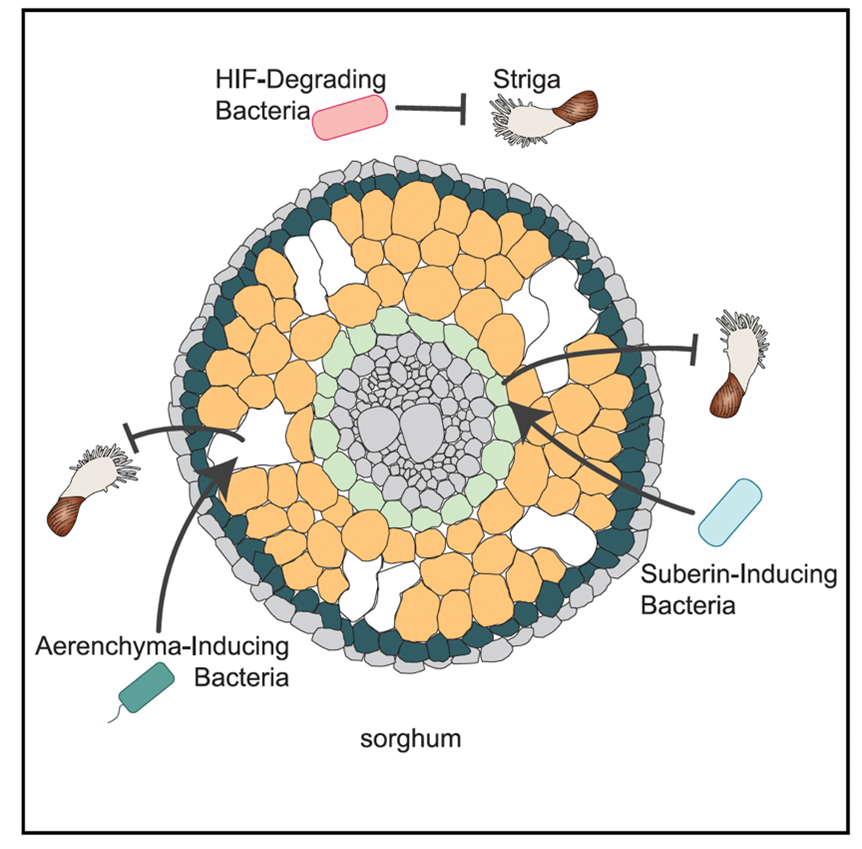
Harnessing the potential of soil microbial allies to combat Striga infection in sorghum roots
Plant Science Research WeeklyMicrobial neighbors of plants in the soil comprise of a vast array of bacteria and fungi, collectively known as the microbiome. This soil microbial community forms close associations with plants and regulates plant growth and development by inducing changes in the plant and soil metabolites. In this…
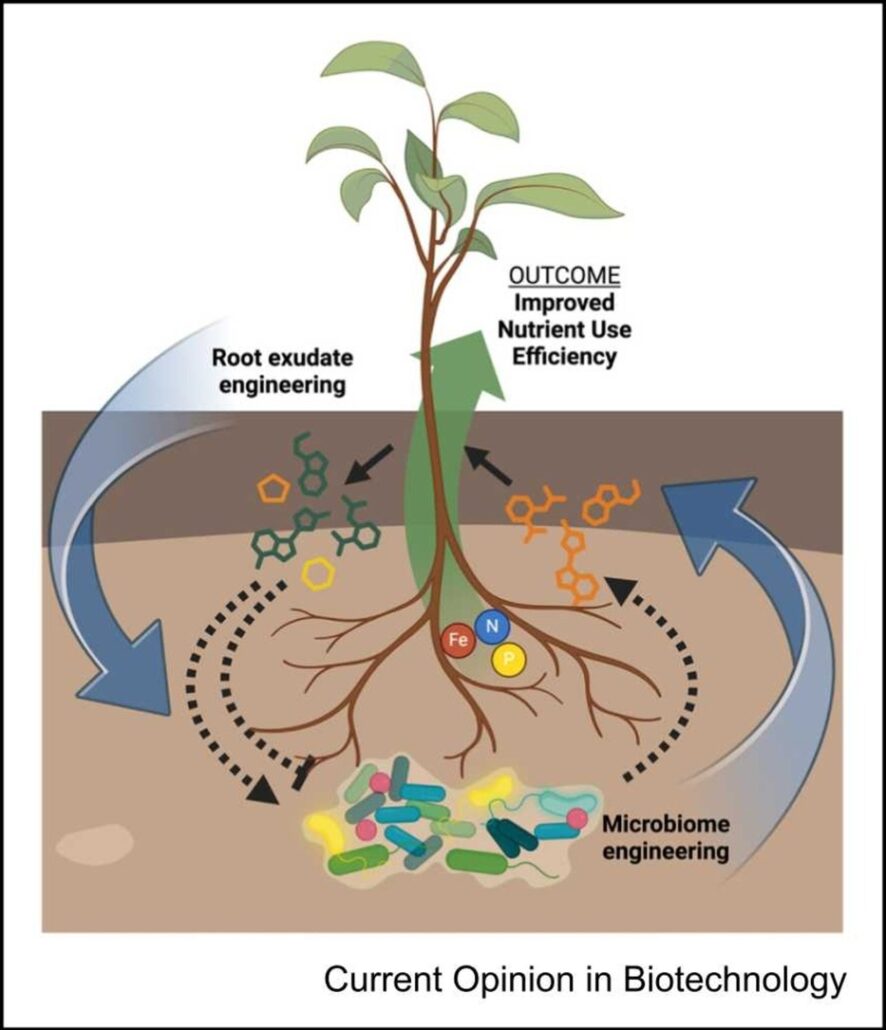
Review: Engineering plant–microbe communication for plant nutrient use efficiency
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant nutrient use efficiency (NUE) has become a major concern in recent years as farmers and scientists strive to make agriculture more sustainable. To this end, the manipulation of plant-microbe interactions holds great potential. In this short review, Griffin et al. highlight recent findings, focusing…
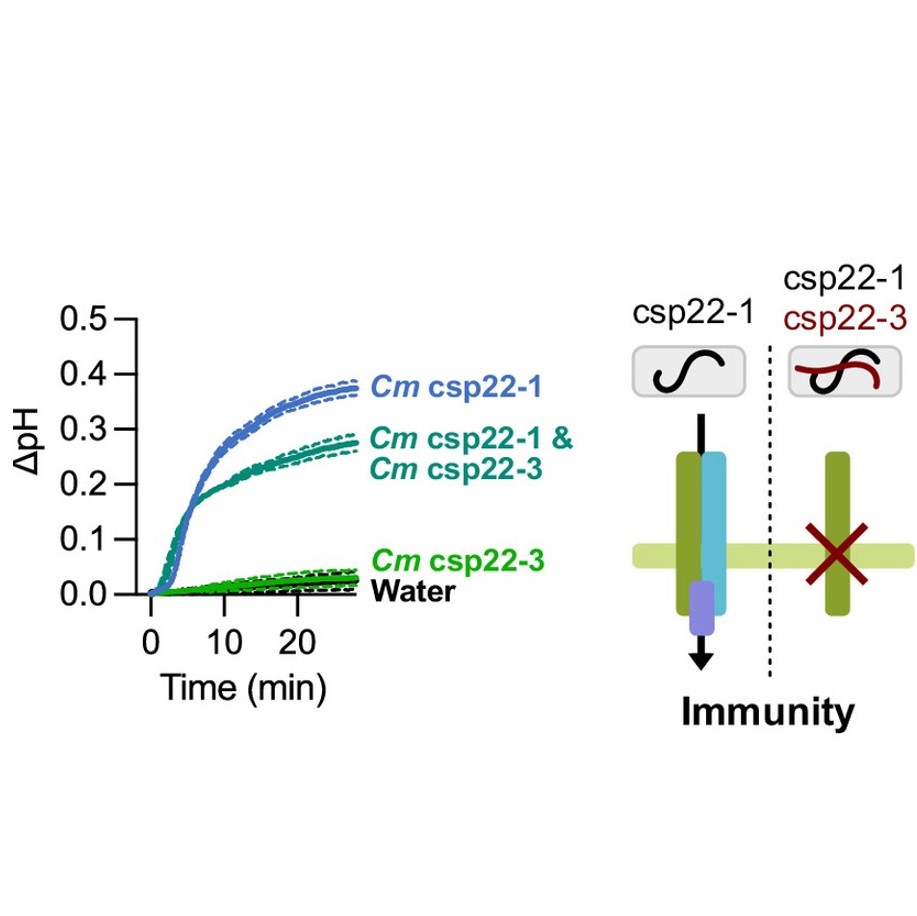
Non-immunogenic bacterial epitopes mask recognition of their immunogenic counterparts
Plant Science Research WeeklyHost plants recognize diverse bacterial epitopes, known as microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs), and respond with an immune reaction to control bacterial growth. However, most studies have focused on single bacterial epitopes, limiting our understanding of plant-bacteria interaction outcomes…
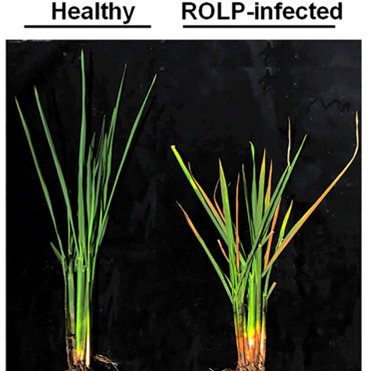
Leaf yellowing phenotype in rice, mediated by phytoplasma-secreted effector protein, attracts insect vectors
Plant Science Research WeeklyPhytoplasmas are bacterial pathogens that induce significant morphological changes in a host plant including prominent leaf yellowing. They are known to be transmitted by piercing-sucking insects or phloem-feeding arthropods. Phytoplasmas alter plant developmental process through specific effectors.…
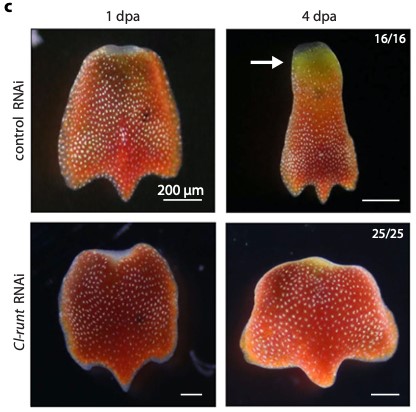
Coordinated wound responses in a regenerative animal-algal holobiont
Plant Science Research WeeklyMany animals such as corals and sea slugs host photosynthetic symbionts. Several studies have investigated how the host and symbiont coordinate their activities. This new study by Sarfati et al. explores how symbiotic green algae and their animal host, the flattened-worm Convolutriloba longifissura,…

