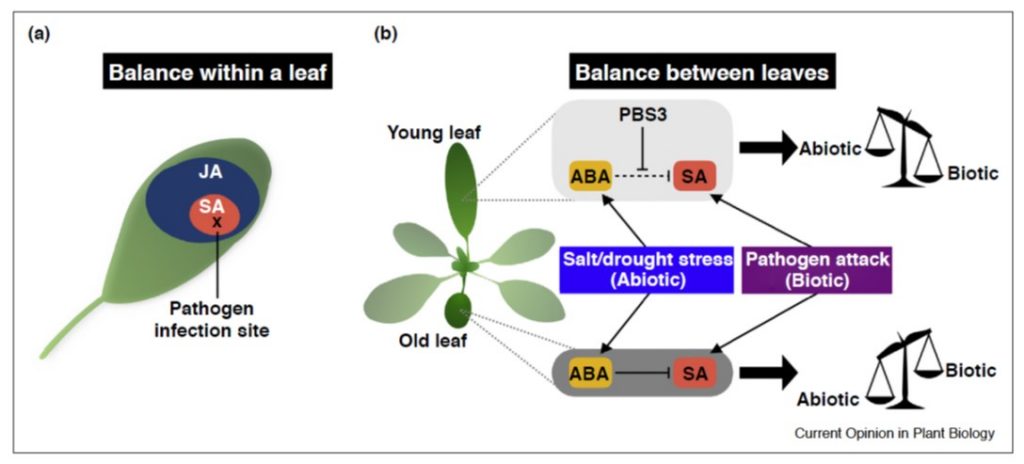
Review: The plant immune system in heterogeneous environments (Curr Opin Plant Bio)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNobori and Tsuda review how the plant immune system is able to function in heterogeneous environments through its properties of resilience, tunability and balance. They define a resilient system as one where “output remains stable even when part of the system is disabled.” Abiotic factors such as…

Detection and stealth at the wall: glycosidases and glycans in flagellin peptide recognition ($) (Science)
Plant Science Research WeeklyBacterial flagellin is a well-known microbial pattern that triggers plant immune responses. Flagellin is a glycosylated protein polymer. The immunogenic domain is buried within the protein structure as well as beneath a glycan layer. Buscaill et al. set out to identify how this immunogenic elicitor is…

Plant Physiology Focus issue on biotic stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe April 2019 issue of Plant Physiology includes a set of papers addressing biotic interactions between plant and pathogens or pests. As the editors indicate, progress on this topic has been rapid and significant. Key topics explored in reviews and research articles include: the roles of plant hormones,…
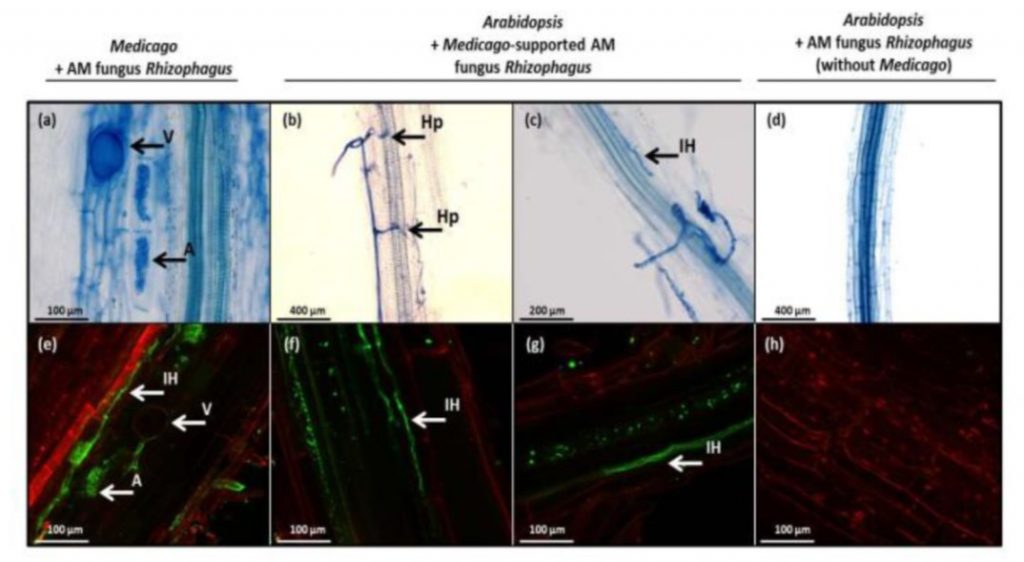
Antagonistic responses to ‘symbiotic’ AM fungi in the non-host Arabidopsis thaliana ($) (New Phytol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA strikingly vast array of phylogenetically distant plants are able to form intimate interactions with symbiotic arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi for the mutually beneficial exchange of nutrients. Several years of intensive research have revealed the complex regulatory networks and genetic ‘toolkits’…

Retargeting of a plant defense protease by a cyst nematode effector ($) (Plant J)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe nematode infection process in plants involves secreted effector proteins that suppress the host defense mechanisms. However, the molecular interactions in which this is done is yet unclear. Here, Pogorelko et al. characterize the function of 4E02, an effector from the cyst nematode H. schachtii,…
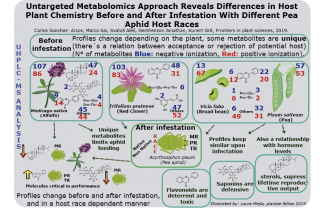
Untargeted metabolomics reveals host plant chemistry before and after pea aphid infestatation (Front. Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPea aphids are genetically diverse, with different biotypes (or “host races”) having different host plant preferences. Sanchez-Arcos et al. reveal several relationships between plant metabolite production and the possibility of colonization of certain aphid host races. Using UHPLC- MS analysis of…
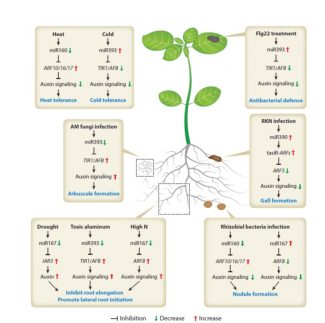
Review: MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plant–environment interactions (Annu Rev Plant Bio) ($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small noncoding RNAs that negatively regulate the expression of target genes through mRNA cleavage, translational repression and DNA methylation. The last decade has seen an exponential increase in the studies performed to understand the biogenesis of plant miRNAs, their…
Review: Linking autophagy to abiotic and biotic stress responses (Trends Plant Sci)($)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAutophagy means “self-eating” in ancient Greek. It’s a process in which cellular components are delivered to lytic vacuoles to be reused. This recycling process promotes abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. In this review, Signorelli et al. highlight in detail plant autophagy in abiotic and biotic…
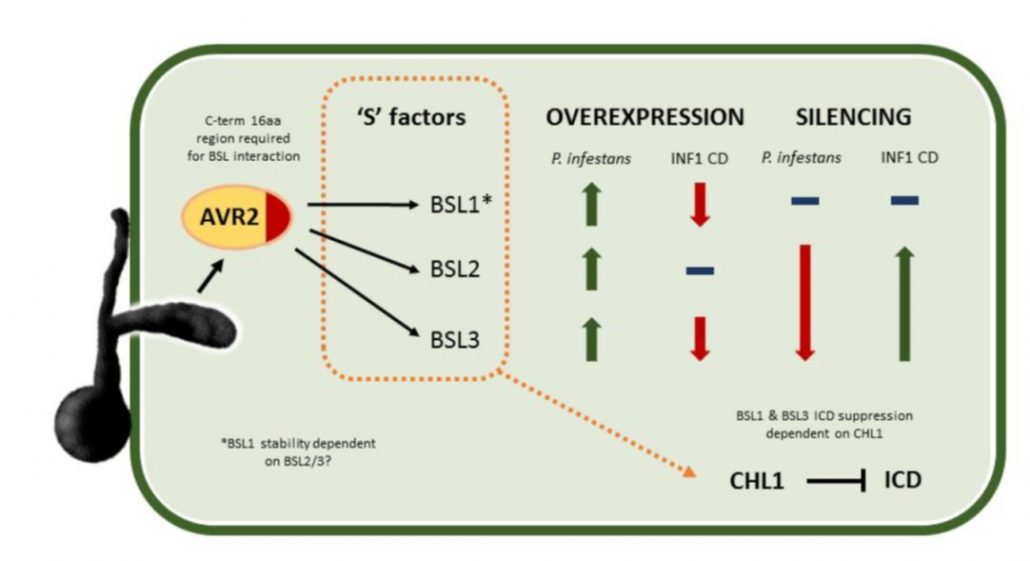
BSL family members are employed by pathogen as “moles” in S. tuberosum (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyTo secure food availability for the world population, plant scientists study the interactions between crop species and pathogens. Plants have robust defense strategies that they employ when attacked. On the other hand, microbes have multiple strategies to manipulate host functions to suppress these defenses…

