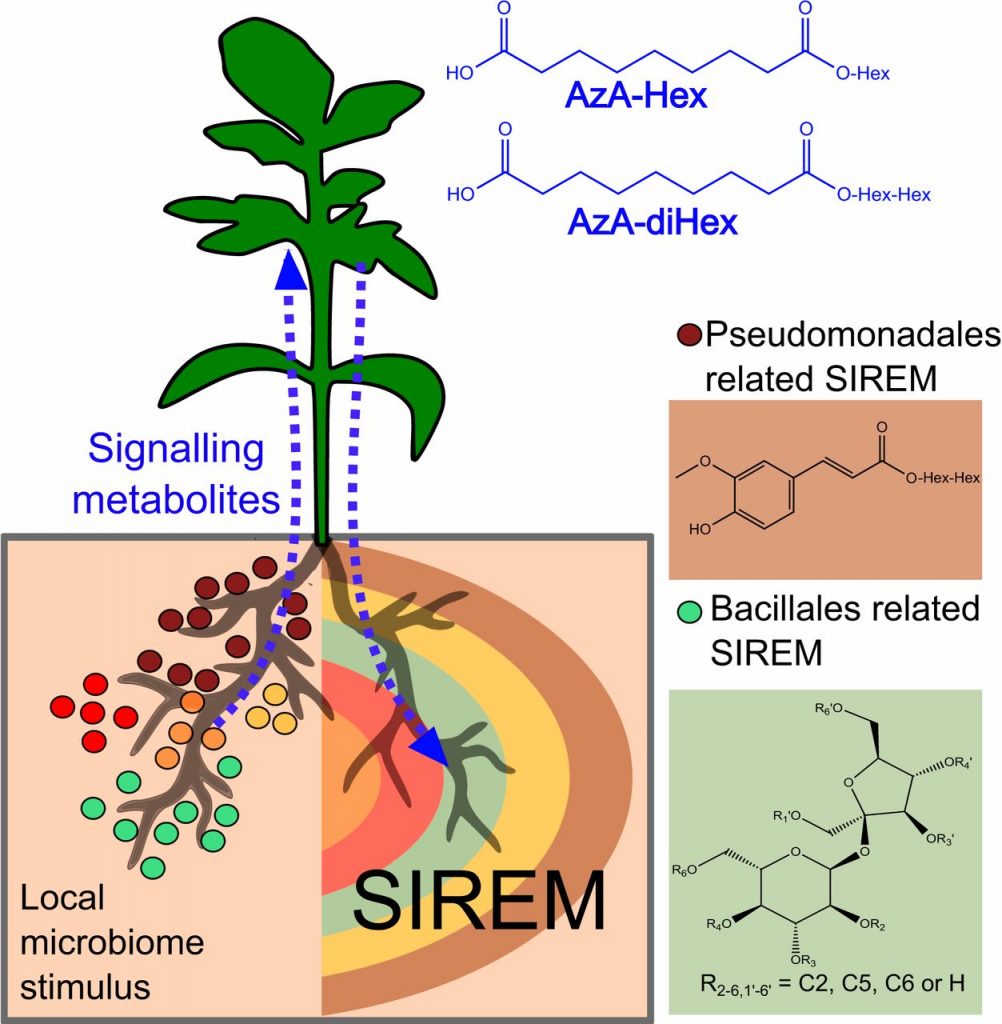
Rhizosphere microbiome mediates systemic root metabolite exudation ($) (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRoots exude metabolites that affect the composition and activities of their microbiome. Korenblum et al. show that the microbiome in turn affects metabolite exudation, not only locally but also systemically (shown using a split-root system). They call this response SIREM: systemically induced root exudation…
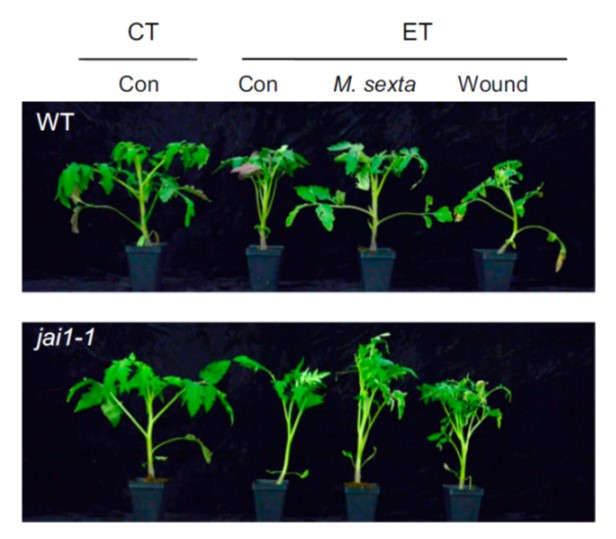
Insect herbivory antagonizes leaf cooling responses to elevated temperature in tomato (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants have strategies to cool themselves when the temperature is hot. These include increasing their rate of transpirational cooling through stomatal opening and raising their leaves, which can enhance air flow. Previous studies have shown a role for the heat shock proteins (HSPs) and their cochaperone…
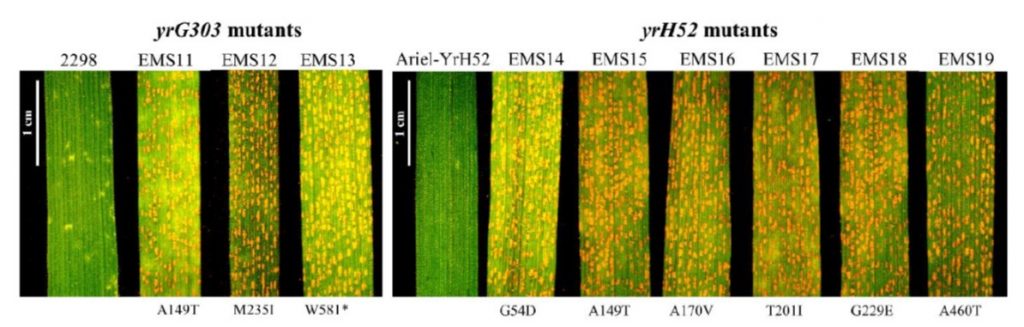
Three previously characterized resistances to yellow rust are encoded by a single locus Wtk1 (J. Exp. Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyYellow rust is a fungal disease of wheat. Three mutants with enhanced resistance were identified in wild emmer wheat from different locations were previously mapped to the same region of chromosome 1B. Given that each locus showed a different degree of resistance, it was presumed that they were non-allelic.…
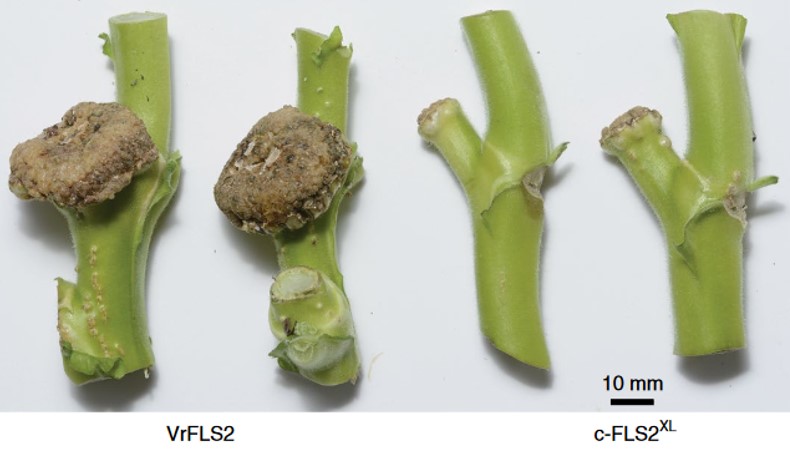

Perception of Agrobacterium tumefaciens flagellin by FLS2XL confers resistance to crown gall disease (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFLS2 is a well-characterized cell-surface receptor that recognizes a short epitope found on most bacterial flagellin proteins. The plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens, causative agent of crown gall disease, deviates strongly at this epitope region, and so is generally not recognized by FLS2 receptors,…
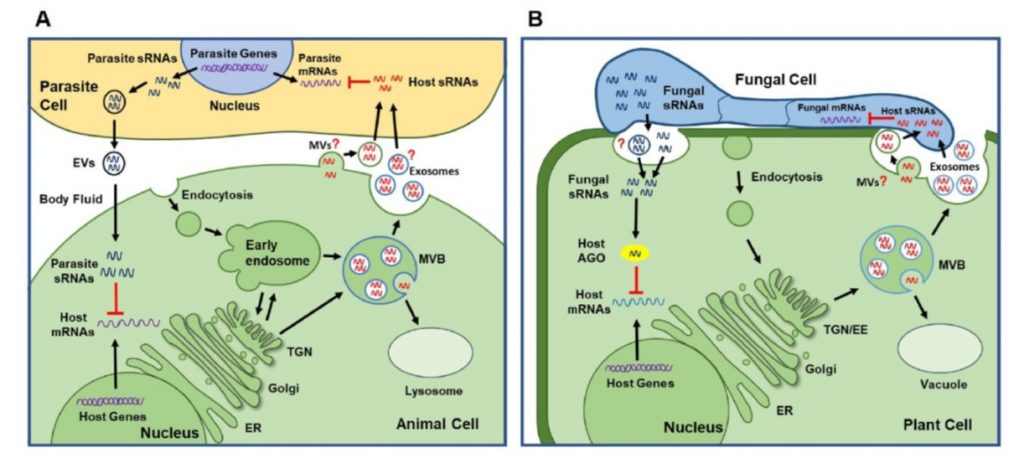
Review. Small RNAs and extracellular vesicles: New mechanisms of cross-species communication and innovative tools for disease control (PLOS Pathogens)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe have only recently begun to appreciate the phenomenon of cross-species or cross-kingdom small RNA transfer, and its applications. Using examples from plants and animals, Cai et al. summarize how some pathogens have evolved the capacity to introduce small RNAs into their host to suppress host defense…
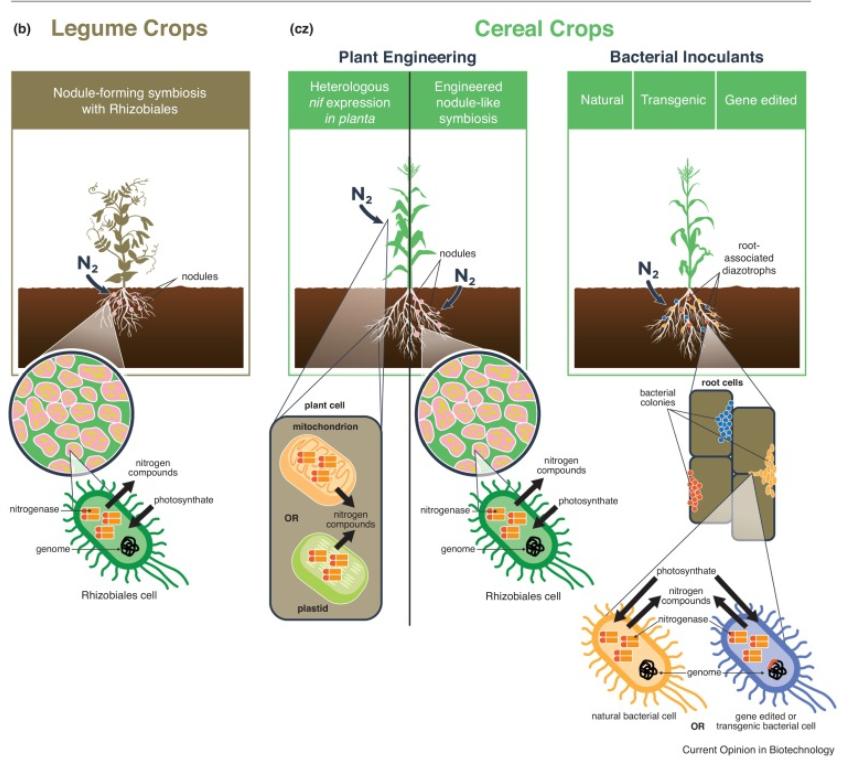
Review: Harnessing atmospheric nitrogen for cereal crop production ($) (Curr. Opin. Biotechnol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyNitrogen demands for plant growth are accomplished through fertilizers or biological nitrogen fixation. Industrial production of nitrogen fertilizer is expensive and causes pollution due to leaching of unused fertilizer. In this review, Bloch et al. discuss the current status of biological nitrogen fixation…
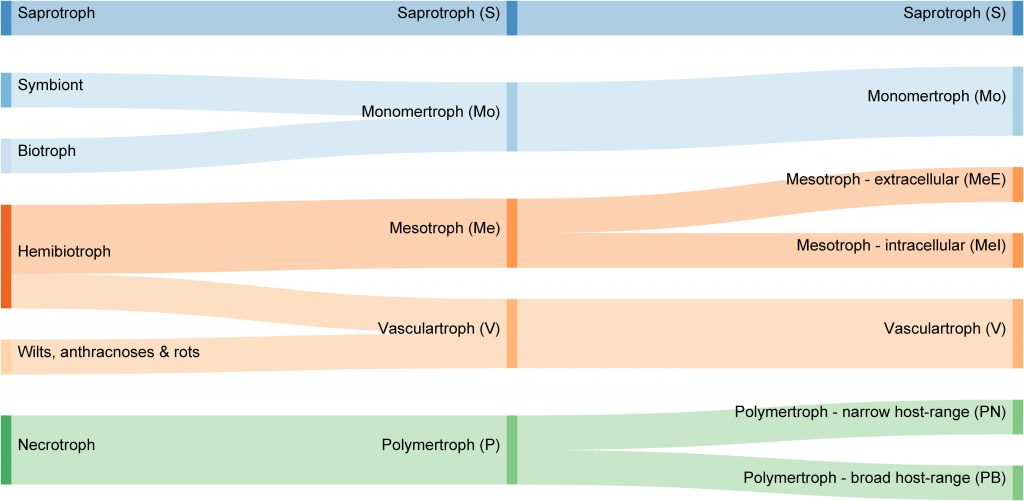
A proposed new classification scheme for fungal and oomycete pathogens based on carbohydrate-active enzymes (Front. Microbiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFilamentous pathogens (fungi and oomycetes) use a variety of tactics to obtain nutrients from plants. Classically, they have been categorized as biotrophic ("eating" living tissues), nectrotrophic (eating dead tissues) or hemibiotrophic (biotrophic followed by heterotrophic). Hane et al. point out that…
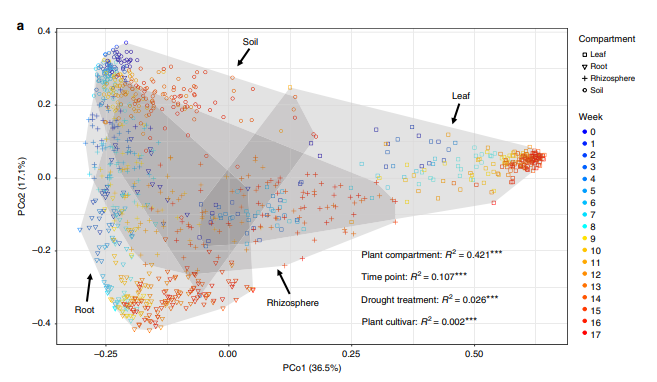
Fungal community assembly in drought-stressed sorghum shows stochasticity, selection, and universal ecological dynamics (Nature Comms)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPreviously, crop-associated mycobiomes were thought to assemble largely under the control of deterministic selection by the plant host with limited influence from drift. This study by Gao et al., highlights the important role of stochastic processes in fungal community assembly, particularly in the hosts’…
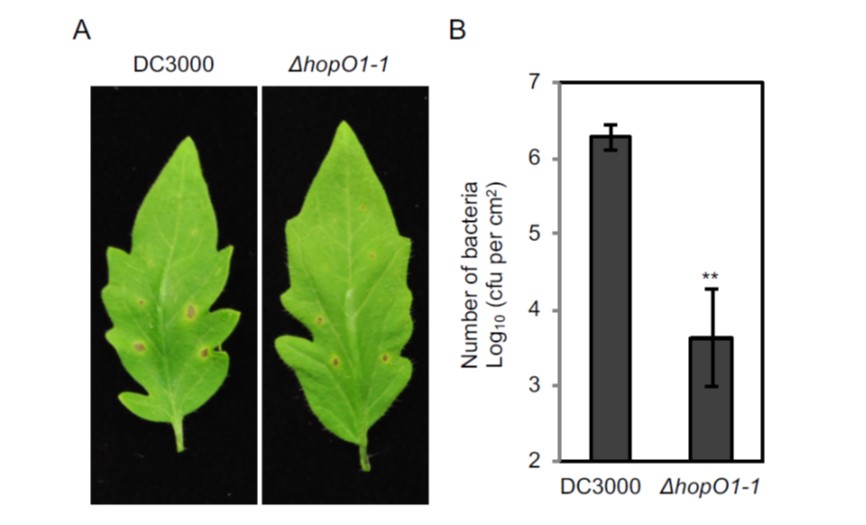
Pathogenic bacteria target plant plasmodesmata to colonize and invade surrounding tissues (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlasmodesmata are regulated channels that connect adjacent cells, allowing movement of metabolites, RNA, proteins, and pathogens. Plants close their plasmodesmata as part of their immune response, but this closure can be interfered with by pathogens. Aung et al. examined the repertoire of effector proteins…

