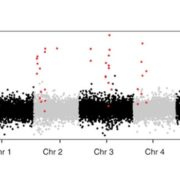
Evolution of transposon-encoded anti-silencing factors in Arabidopsis ($)
Transposable elements (TEs) are a major component of eukaryotic genomes. Their activity is silenced by epigenetic mechanisms such as chromatin modifications and DNA methylation in order to avoid deleterious effects on host genome stability. Nevertheless, how TEs overcome silencing by the host and propagate…

KNS4/UPEX1: A Type II Arabinogalactan β-(1,3)-Galactosyltransferase Required for Pollen Exine Development
Pollen is an essential component in angiosperm reproduction. Pollen grains are surrounded by a highly resistant wall called exine which enables survival of the male gametes in adverse environmental conditions. Suzuki et al. examined the contribution of an Arabinogalactan β-(1,3)-Galactosyltransferase…
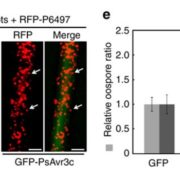
An oomycete plant pathogen reprograms host pre-mRNA splicing to subvert immunity
Phytopthora sojae poses a serious threat to soybean production world-wide. This oomycete pathogen has a wide arsenal of effector proteins, some of which have been functionally characterized for their virulence role. Huang et al. characterized and demonstrated the functional role of an avirulence effector…
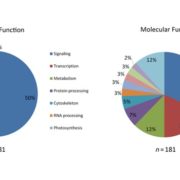
Oh, the places they’ll go! A survey of phytopathogen effectors and their host targets ($)
All phytopathogens encode for a toolbox of secreted proteins called ‘effectors’ that promote disease formation in the best possible way. Effectors are either acting in the apoplastic space or are translocated to the host cell to target diverse processes and modulate the host using enzymatic activities.…
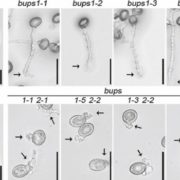
Arabidopsis pollen tube integrity and sperm release are regulated by RALF-mediated signaling
Successful fertilization in plants requires sperm cells (SCs) to be carried along the growing pollen tube (PT) until reaching the female gametophyte where the PT then bursts to release the SCs. One challenge PTs must overcome in order to achieve fertilization is deciding to rupture or not to rupture.…
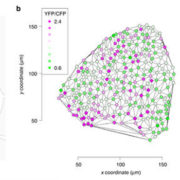
Stochastic gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana
Biology is a noisy act, as the expression of the same gene in the cells of the same tissue differs. This noise can be divided into intrinsic noise, due to inherent stochasticity of molecular processes, and extrinsic noise, indicating differences between the neighboring cells. Schultheiß Araújo and…
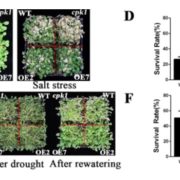
Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinase AtCPK1 plays a positive role in salt/drought-stress response ($)
Ca2+-dependent protein kinases (CPKs) can transfer calcium signals via phosphorylation events, a signaling process important for plant development and response to environmental stresses. With the multitude of CPKs thus far identified and their overlapping roles in both abiotic and biotic stress response,…
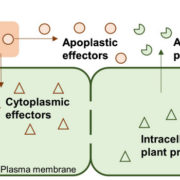
APOPLASTP: prediction of effectors and plant proteins in the apoplast using machine learning ($)
The apoplast represents a highly interactive site for intercellular communication and transport in plant-microbe interaction, that determines whether a pathogen can successfully overcome the early stages of plant defense. This site is also a battleground for an important class of apoplastic effectors…
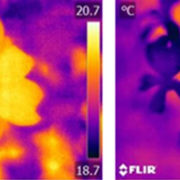
The diversity of floral temperature patterns, and their use by pollinators
Bees and other pollinators experience the world in a different way to humans. They use different strategies in order to identify their surroundings, including their preferred flower species. Among these strategies, floral temperature. These differential “floral warming” happens due to floral thermogenesis…

