The fate of scent in insect- vs. wind-pollinated flowers ($) (Ann. Bot)
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlower traits (mainly flower colour, position, shape, size, reward and scent) in present-day plants are the result of past selection pressures. Among these traits, scent is a crucial component mediating pollinator attraction, and is often greatly reduced in abiotic-pollinated plants. Wang et al. characterize…
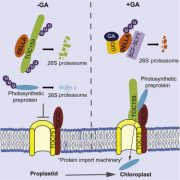
Chloroplast biogenesis controlled by DELLA-TOC159 interaction in early plant development (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast, the green organelles that are the most famous members of the plastid family. Chloroplast biogenesis starts with illumination at germination, when the colorles, non-photosynthetic proplastid acquires photosynthetic activity as it greens. Gaining photosynthetic…

A single cis-element that controls cell-type specific expression in Arabidopsis (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMulticellular organisms have different tissues that carry out diverse and specialized functions, and tissue-specific expression is the feature that gives each tissue its specific protein content. Despite its importance, the mechanisms that control spatial patterning is poorly understood. In this work,…
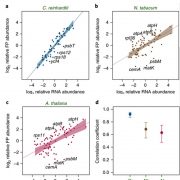
Divergent strategies to maintain steady state protein levels in algal and angiosperm chloroplasts (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants and their algal predecessors both utilize chloroplasts for photosynthesis and other essential metabolic processes. The endosymbiotic origin and subsequent co-evolution of this autotrophic organelle introduced striking regulatory mechanisms combining both prokaryotic and eukaryotic strategies for…

Review: MYBs drive novel consumer traits in fruits and vegetables (Trends Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe MYB transcription factors, specifically the R2R3 family of MYBs, are closely associated with the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis. This easy-to-score trait made MYBs some of the earliest characterized plant transcription factors. Allan and Espley summarize the contributions of MYBs to pigmentation…
Roles of N-terminal acetylation and N-terminal acetyltransferases in plants (J. Exp. Bot.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyN-terminal acetylation is a common protein modification completed by ribosome-associated N-terminal acetyltransferases (NATs) or plastid-localized NATs. The recent discovery of the plastid-localized NATs upended the traditional model of static, co-translational imprinting of the plant proteome. These…
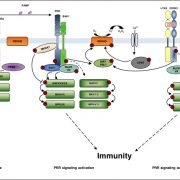
Review: Regulation of pattern recognition receptor signalling by phosphorylation and ubiquitination (Curr. Opin. Plant Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyA key step in pathogen recognition occurs at the cell surface with the interaction between receptor-like kinases (pattern-recognition receptors) and their ligands. This event triggers a signal-transduction cascade that leads to the induction of defense responses. Mithoe and Menke review our current understanding…
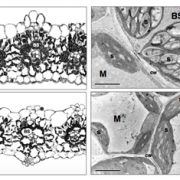
Diffusion of CO2 across the mesophyll-bundle sheath cell interface in a C4 plant with genetically reduced PEP carboxylase activity (Plant Physiol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyC4 photosynthesis relies on the transport of carbon (in the form of C4 acids) from the mesophyll into bundle sheath cells (BSCs). Subsequent decarboxylation of these C4 acids generates a high concentration of CO2 in the vicinity of Rubisco, helping to improve the catalytic efficiency of this enzyme. …
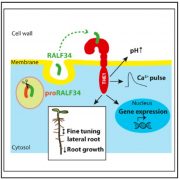
Receptor kinase THESEUS1 is a RALF 34 receptor with roles in lateral root development (Curr. Biol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyRALF peptides were identified nearly 20 years ago, as small peptides that induce rapid alkalinisation of the culture medium when added to cell suspension cultures. Previously, members of the receptor-like kinase (RLK) family including FERONIA (FER) have been identified as RALF receptors. A related…

