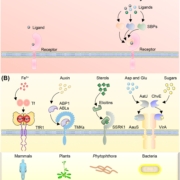
Plant surveillance: The emerging role of substrate-binding proteins
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants are sessile organisms and, unlike animals, cannot escape adverse environmental conditions. To cope with this limitation, they have evolved a complex surveillance system to detect and respond to fluctuating conditions such as resource scarcity, environmental changes, and pathogen attacks. Membrane-bound…
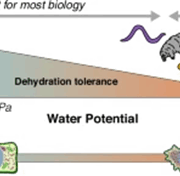
Perspective. The art of drying gracefully: The future for desiccation research
Plant Science Research WeeklyIn their perspective article, “Life on the dry side: a roadmap to understanding desiccation tolerance and accelerating translational applications,” Marks et al. outline the current state and future promise of desiccation tolerance research. They define desiccation tolerance as “the ability to dry…
Review: Translating research from Arabidopsis to crops
Plant Science Research WeeklyThis year marks the 25th anniversary of the publication of the Arabidopsis genome, a milestone that lives large in those of us who experienced it and eagerly envisioned how this new knowledge would be used. The May 2025 issue of The Plant Cell focuses on how research on this little model plant has translated…
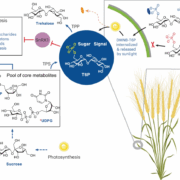
Rewiring sugar signaling for global agriculture: A decade of progress in harnessing the T6P pathway
Plant Science Research Weekly, Uncategorized
Rewiring sugar signaling for global agriculture: A decade of progress in harnessing the T6P pathway
While sugar signaling plays a crucial role in grain filling and ultimately determines grain crop yield, direct genetic manipulation often results in pleiotropic effects and raises legislative…
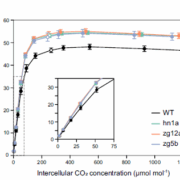
Boosting C4 photosynthesis and productivity by elevating Rubisco levels in sorghum and sugarcane
Plant Science Research WeeklyThe United Nations projects that by 2050, global food production must increase by 60% to meet growing demand, a goal that must be met under the pressures of global climate change and without further agricultural land expansion. With rising atmospheric CO₂ levels, Rubisco has emerged as the primary…
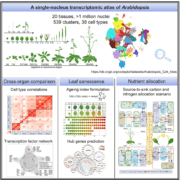
Leaf senescence mapped through Arabidopsis single-nucleus RNA-Seq atlas
Plant Science Research WeeklyAs both the power and accessibility of single-cell RNA sequencing increases, more reference datasets have become available, documenting the transcriptome within a variety of model plants. While invaluable resources that have pushed science forward, these datasets are often limited to single tissues or…
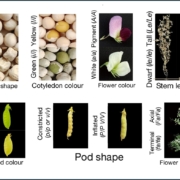
Identification of the final set of Mendel’s pea genes
Plant Science Research WeeklyWe can be assured that every biology student is exposed to plants at least once, when they learn about the genetic laws that Mendel formulated from his studies on peas. His classic work focused on seven traits that exhibited simple dominant-recessive characteristics, such as seed color and shape and…
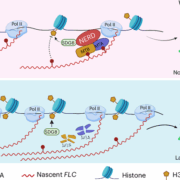
Unraveling the epitranscriptomic-chromatin axis: How NERD regulates flowering in Arabidopsis
Plant Science Research WeeklyFlowering in Arabidopsis thaliana is governed by complex genetic and epigenetic networks. A central component of this regulation is the floral repressor FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC), whose expression is modulated by histone modifications, particularly the activating H3K36me3 and the repressive H3K27me3 marks.…
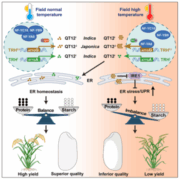
Cracking the code of rice grain quality under heat stress
Plant Science Research WeeklyRice is one of the most important food crops globally, providing more than 20% of the world’s calorie intake and over 75% for the population in Asia. Therefore, apart from yield, grain quality is another critical agronomic trait for breeding and improvement, especially under stressful environmental…

