
Non-CG methylation mechanism in Marchantia polymorpha ($) (Plant Cell Physiol.)
Previous reports have shown that M. polymorpha DNA methylation status varies during its life cycle and it contains only one copy of the METHYLTRANSFERASE1 (MET1) orthologous gene. MET1 is responsible of CG methylation in angiosperms. Ikeda and collaborators generated MpMET mutants using the CRISPR/CAS9…
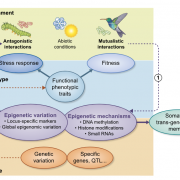
Review: The role of plant epigenetics in biotic interactions (New Phytol.)
Plant phenotypes are influenced by the nature and intensity of biotic interactions. While the role of genetic diversity has been extensively studied, contribution of epigenetics to plant fitness and response to biotic stresses remains elusive. The authors review here the most recent literature about…

Digital imaging combined with genome-wide association mapping links loci to plant-pathogen interaction traits (Plant Phys.)
Resistance to plant pathogens is often studied as a qualitative trait than quantitative, focusing on the lesion size and pathogen numbers. However, resistance to generalist plant pathogens, such as Botrytis cinerea, is known to involve multiple genes. Fordyce et al. used high-throughput phenotyping…
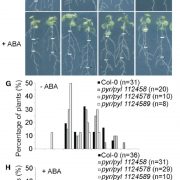
The xerobranching response represses lateral root formation when roots are not in contact with water (Curr. Biol. - $)
Roots navigate through the soil, foraging for water and nutrients. Orman-Ligeza et al. observed that lateral root development is repressed when the roots are growing through the soil air spaces. Exposure to water deficit induced transcriptome reprogramming in barley roots of genes involved in many hormone…
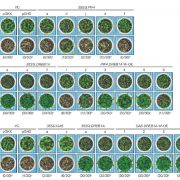
A gene‐stacking approach to overcome the trade‐off between drought stress tolerance and growth in Arabidopsis (Plant J)
In the face of increasing incidence of drought events, developing drought-tolerant plants becomes urgent matter. However, the increase in drought tolerance often coincides with the significant reduction of plant size, as in the case of overexpressing DEHYDRATION-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT-BINDING PROTEIN 1A…
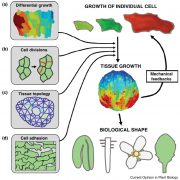
Review - Cellular basis of growth in plants: geometry matters (COPB - $)
Plants exhibit various forms which are determined by the individual cells. The diversity of cell shapes within a single organism is astounding and results from the interactions between the pressure generated by the cell and surrounding tissue as well as heterogeneities in the cell wall composition. As…

A plant chitinase controls cortical infection thread progression and nitrogen-fixing symbiosis (eLIFE)
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria produce species-specific chitin-like molecules, Nod factors, which induce nodule development and infection thread formation in the host plant, aiding microbial infection. Malolepszy et al. performed a detailed study of symbiotic defective mutants in lotus (chit5), where the nodule…
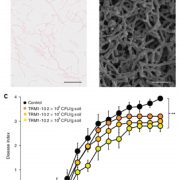
Rhizosphere microbiota structure alters to enable wilt resistance in tomato (Nature Biotech. - $)
Plants are frequently attacked by pathogens, but the pathogen-resistance is often attributed to the host. While interactions between the plant and its microbiota are recognized for their role in plant growth, their role in pathogen resistance is unknown. Kwak et al. studied the effect of soil-borne pathogen Ralstonia…
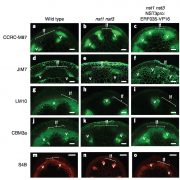
Complete substitution of a secondary cell wall with primary cell wall in Arabidopsis (Nature Plants - $)
Plant cell walls are important for terrestrial lifestyle, providing support and directing the plant growth. The primary and secondary cell walls differ in their chemical composition and flexibility. Secondary cell walls are less perceptive to industrial degradation processes and therefore pose problems…

