
The role of ER stress-depending autophagy under phosphate deprivation (Plant Physiol)
In the Brassicaceae, inorganic phosphate (Pi) deprivation modifies root system architecture to favor Pi foraging, through the inhibition of primary root growth and the stimulation of lateral root growth. Root growth inhibition is triggered by Fe-stimulated ROS generation and cell wall modifications,…
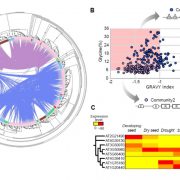
Genomic diversification of LATE EMBRYOGENESIS ABUNDANT (LEA) protein gene families (GBE)
LEA genes were first identified as being highly abundant during seed desiccation (hence their name), but later were also shown to accumulate in other tissues in response to drought stress, and to confer desiccation tolerance in “resurrection plants”. These small proteins are characterized by having…
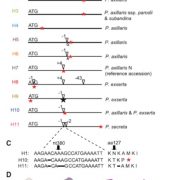
Pseudogenization and resurrection of a speciation gene (Curr. Biol)
Many flowers have evolved to attract pollinators through scent, shape, nectar production and color. Small changes in any of these attributes can be sufficient to dramatically shift pollinator preferences and pollination efficiency. Petunia has recently diverged into several species, characterized as…

Synthetic apomixis: Asexual propagation through seeds (Nature) ($)
Sexual reproduction mixes up genes and provides genetically diverse progeny, key for survival and fodder for evolution. Sexual reproduction is detrimental to the propagation of hybrid crops though, as mixing up the genes leads to progeny that will be inferior to the hybrid parent. Khanday et al. have…
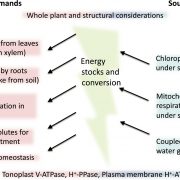
Meeting review: Energy costs of salinity tolerance in crop plants (New Phytol)
Plants use diverse strategies for salt tolerance, including regulated transport of several different ions and production of compatible organic solutes. In April 2018, a workshop was held to discuss strategies for breeding salt tolerance in plants, with a focus on the energy requirements of various strategies.…
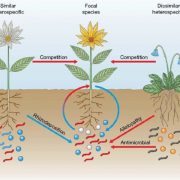
Review: Mechanisms of plant–soil feedback: interactions among biotic and abiotic drivers
We often think about how the soil environment influences plants, but two new papers focus on how plants influence the soil environment (through abiotic and biotic effects), in turn affecting other plants. These plant-soil feedbacks (PSFs) can be negative (resource depletion, natural enemy accumulation)…
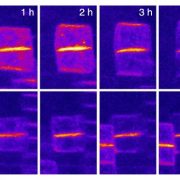
Re-establishment of PIN2 polarity after cell division (Nature Plants)
Plant cells have polarity, with the distribution of the auxin transporter protein PIN2 being a well-described example. Glanc et al. investigated how polarity is re-established following cell division. The authors showed that during cytokinesis, protein trafficking is directed towards the central cell…
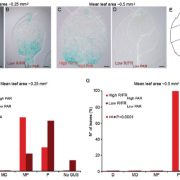
Leaf development in canopy shade (J. Exp. Bot)
Vegetative shade affects the ratio of red (R) and far-red (FR) light; relative to sunlight, the R/FR ratio is decreased due to absorbance of photosynthetically-active R light by other leaves. Low R/FR ratios cause increased elongation of shaded plant stems and petioles, as the plants strive to raise…
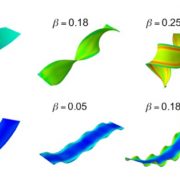
Differential growth and shape formation in plant organs (PNAS)
This paper is kind of fun because it explores plant leaf and petal shape from an engineering perspective, identifying “fundamental mechanistic insights into how nature invokes mechanics in the evolution of commonly found shapes in plant organs by differential growth.” For each organ, the authors…

