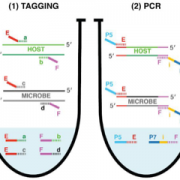
Measuring both microbial load and diversity with a single amplicon sequencing library (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAmplicon sequencing of microbial DNA is a gold standard for analyzing the relative abundance of microbes in host-associated microbiomes. To gain more accurate insights into microbiome changes, it is crucial to know the absolute abundance of microbes, which can be analyzed by integrating relative abundance…
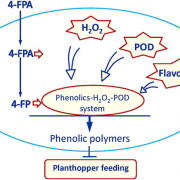
A chemical elicitor, 4- fluorophenoxyacetic acid suppresses insect pest populations and increases crop yields (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlant strengtheners, synthetic chemical elicitors, have been shown to enhance plant resistance against various insect pests without toxic effects on the environment, but evidence is lacking for a significant increase in crop growth and yield after using these elicitors. To address this, Wang et al. studied…
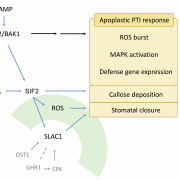
STRESS INDUCED FACTOR 2 regulates arabidopsis stomatal immunity through phosphorylation of the anion channel SLAC1 ($) (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants detect microbes by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that sense common conserved structures called microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) and trigger the innate immunity responses. Chan et al. identified a new player in the Arabidopsis immune response known as STRESS INDUCED FACTOR 2…
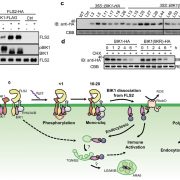
Ligand-induced monoubiquitination of BIK1 regulates plant immunity (Nature)
Plant Science Research Weekly
The plant immune system has been a keenly researched area in plant sciences in the past decade. Elicitors present in microbes are compounds that induce response from plants when under attack. These elicitors are conserved in many pathogens and are called microbe associated molecular patterns (MAMPs).…
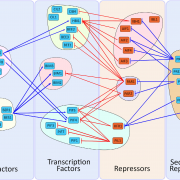
Review: The bHLH network underlying plant shade-avoidance (Physiol. Plant.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyShade avoidance is a complex phenomenon in which plants avoid shade by altering their developmental program in various ways including early flowering, hypocotyl elongation, and more. Many photoreceptors and transcription factors (TFs) are involved in regulating shade avoidance, including the bHLH (basic…
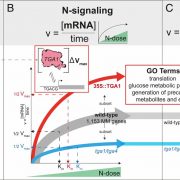
Nutrient dose-responsive transcriptome changes driven by Michaelis–Menten kinetics underlie plant growth rates (PNAS)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants can increase their growth and biomass proportionately to an increase in nutrient dose and, conversely, their growth is limited by limiting nutrients. In this study, Swift et al. explored the molecular underpinnings of the nutrient dose-response phenomenon. The authors first show that nitrogen-dose…
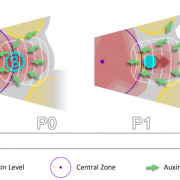
How do auxin temporal dynamics regulate patterning? (eLIFE)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin forms spatial gradients that are implicated in organ morphogenesis. However, it is not known how temporal auxin gradients are integrated with the spatial information. In this paper, Galvan-Ampudia, Cerutti et al., showed using a ratiometric quantitative auxin reporter (quantitative DII-VENUS) that…
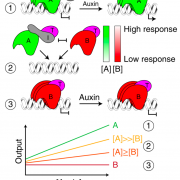
Design principles of a minimal auxin response system (Nature Plants)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAuxin controls virtually all facets of growth and development. This plant hormone is sensed by TIR1/AFB F-box receptors which promote ubiquitin-mediated degradation of AUX/IAA transcriptional repressors, releasing ARF transcription factors from inhibition. Phylogenetic analyses divide the ARF family…
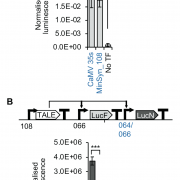
Plant synthetic promoters to fine tune expression of engineered genes (bioRxiv)
Plant Science Research WeeklySynthetic genetic circuits allow the reconstruction of metabolic pathways in plant systems for production of many natural products including pharmaceuticals. A challenge in genetic engineering these circuits is precisely and predictably regulating gene expression, especially when genes may be desired…

