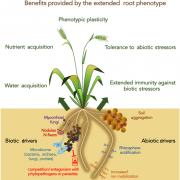
Review: An extended root phenotype: the rhizosphere, its formation and impacts on plant fitness (Plant J.)
The rhizosphere is a continuous space for microbial colonization that comprises the rhizospheric soil, the rhizoplane (root surface), and the root endosphere, which is the apoplastic space in the root cortex. It is inhabited by unique populations of microorganisms, influenced by plant genotype and the…
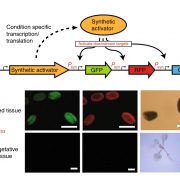
Modulation of gene expression in plants with orthogonal regulatory systems (Nat. Chem. Biol.)
Some of the most promising applications in synthetic biology need precise control of gene expression. For instance, metabolic engineering in plants requires the expression of enzyme-coding genes at a precise time, space, and quantity to ensure correct output. Recently, Belcher, Vuu, and colleagues engineered…
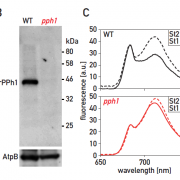
Role of two phosphatases in state transition of Chlamydomonas (Plant Physiol.)
Plants and green algae can rapidly adapt to changing light conditions. Depending on light availability or other metabolic needs, Light Harvesting Complexes (LHC) II can be reallocated to photosystem I (PSI) from photosystem II (PSII) and vice versa. This is known as state transition and is mediated by…
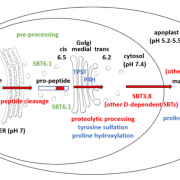
The biogenesis of CLEL peptides involves several processing events in consecutive compartments of the secretory pathway (eLIFE)
Small signaling peptides are cleaved from precursor proteins by the action of proteases and are also subject to other post-translational modifications. Subtilases (SBT) are mostly extracellular proteases, but SBT6.1 is membrane-localized at the Golgi and plasma membranes. Furthermore, it has been shown…
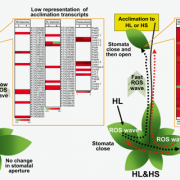
Systemic signaling during abiotic stress combination in plants (PNAS)
In nature, plants face multiple environmental stresses simultaneously. Plant responses to combined stresses are often not merely the sum of responses to individual stresses; in the tissue that initially perceive stresses (local tissue), plants can integrate different stress signals to elicit unique responses.…
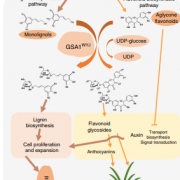
UDP-glucosyltransferase regulates grain size and abiotic stress tolerance associated with metabolic flux redirection in rice (Nature Comms.)
Climate change severely affects plant growth and jeopardizes yields of essential seed crops such as rice. Still, the mechanisms underlying the synergistic regulation of abiotic stress response and important agronomic traits remain poorly understood. Dong et al. cloned and characterized a major QTL in…
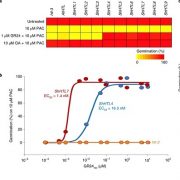
SMAX1-dependent seed germination bypasses GA signalling in Arabidopsis and Striga (Nature Plants)
Strigolactones (SL) are germination cues for parasitic plants, as their seeds will not germinate until they perceive SL exuded from the host plant. In contrast, gibberellins (GA) are the dominant germination hormone in non-parasitic plants; GA-mediated degradation of DELLA repressors permits germination.…
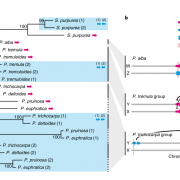
A single gene underlies the dynamic evolution of poplar sex determination (Nature Plants)
Dioecy (male and female flowers residing on distinct individuals) has independently arisen several times in angiosperms, yet the genetic basis of dioecy remains obscure. Here, Müller et al. reveal a single gene that acts as a sex-determination switch throughout the Populus genus. A negative regulator…
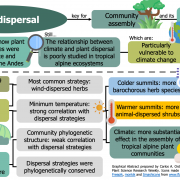
Plant dispersal strategies of high tropical alpine communities across the Andes (J. Ecol.)
Since dispersal is crucial for the assembly of plant communities, a better understanding of its relation to climate is needed to predict plant communities' responses to changes in the environment. However, this kind of association is still missing in tropical alpine ecosystems –one of the most vulnerable…

