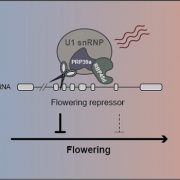
An RNA splicing factor regulates temperature-responsive flowering
The Plant Cell: In a NutshellChang et al. discover the role of an evolutionarily conserved splicing factor in regulating temperature-responsive flowering in Arabidopsis.
Background: Eukaryotic genes contain non-coding sequences termed introns that intervene between coding sequences. After being transcribed into pre-mRNA, these…
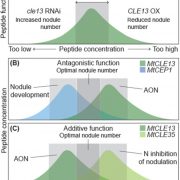
Review: A rulebook for peptide control of legume–microbe endosymbiosis (Trends in Plant Sci)
Plant Science Research WeeklySymbiotic associations with bacterial or fungal partners enhance nutrient uptake for most plants, and recent years have uncovered the very sophisticated means by which these associations are established and controlled. Peptides have emerged as key regulators of many facets of mycorrhizal and rhizobial…
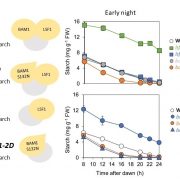
A dominant mutation in β-AMYLASE1 disrupts nighttime control of starch degradation in Arabidopsis leaves (Plant Physiol)
Plant Science Research WeeklyPlants use starch in leaf chloroplasts to fuel their growth and metabolism during the night. In Arabidopsis, nighttime starch degradation is tightly regulated; the degradation rate is linear and adjusts to both the availability of starch and length of night, so that most but not all the starch is used…
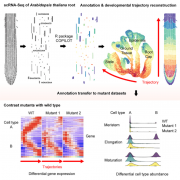
A single-cell Arabidopsis root atlas reveals developmental trajectories in WT and cell identity mutants (Dev. Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklySingle-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is a powerful tool to identify rare and novel cell types, characterize multiple cell types, and more accurately understand their functions across their life cycles. The Arabidopsis root is a perfect system in which to investigate cellular differentiation due to…
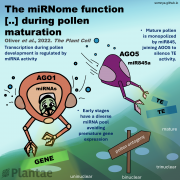
The miRNome function transitions from regulating developmental genes to transposable elements during pollen maturation (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyGenes (protein-coding or noncoding) and transposable elements (TEs) are the main characters in the genomic landscape, but there are few reported systems where we have seen all acting together to produce a phenotype. Oliver and collaborators analyzed miRNA populations during pollen maturation in an outstanding…

The MIEL1-ABI5/MYB30 regulatory module fine tunes abscisic acid signaling during seed germination (JIPB)
Plant Science Research WeeklyAbscisic acid (ABA) is a phytohormone that plays a crucial role in the inhibition of seed germination, and the transcription factor ABI5 is the final and common downstream factor that represses germination. Many proteins are known to inhibit ABI5, such as the mediator complex subunit MED25 or other transcription…

Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 5 mediated by nitric oxide suppresses ethylene biosynthesis in apple fruit (New Phytol.)
Plant Science Research WeeklyMechanisms of phytohormone modulation and their interface with other regulatory molecules are still being uncovered. Nitric oxide (NO) is a regulatory molecule which has been shown to affect ethylene biosynthesis through the action of ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 5 (ERF5) in apple fruit. New work by Ji et…
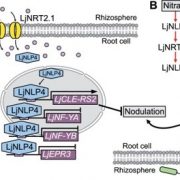
Nitrate transporter NRT2.1 is a determinant of a nitrogen acquisition switch between nitrate uptake and symbiosis in Lotus japonicus (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyWhen nitrogen or nitrate availability is high, symbiotic nodule generation is curtailed to conserve the associated energy cost. But how does the presence of nitrate interfere with nodulation and symbiosis? Previously, genetic studies identified nitrate unresponsive symbiosis (nrsym) mutants in Lotus…

Arabidopsis CHROMATIN REMODELING 19 acts as a transcriptional repressor and contributes to plant pathogen resistance (Plant Cell)
Plant Science Research WeeklyChromatin remodellers are highly conserved eukaryotic proteins with regulatory roles in various aspects of DNA metabolism including DNA repair, gene expression and mitosis. Here, Kang et al. examine the function of the CHROMATIN REMODELLING19 (CHR19) in Arabidopsis thaliana. Using two T-DNA insertion…

