Special Issue: Long-distance signaling ($) (Plant Cell Physiol)
Of course plants need to communicate between their different parts, and our understanding of these crucial signals has been advancing rapidly. This issue of Plant Cell Physiology includes a set of papers highlighting recent findings. A meeting report by Kiba on the Integrative Graduate Education and…
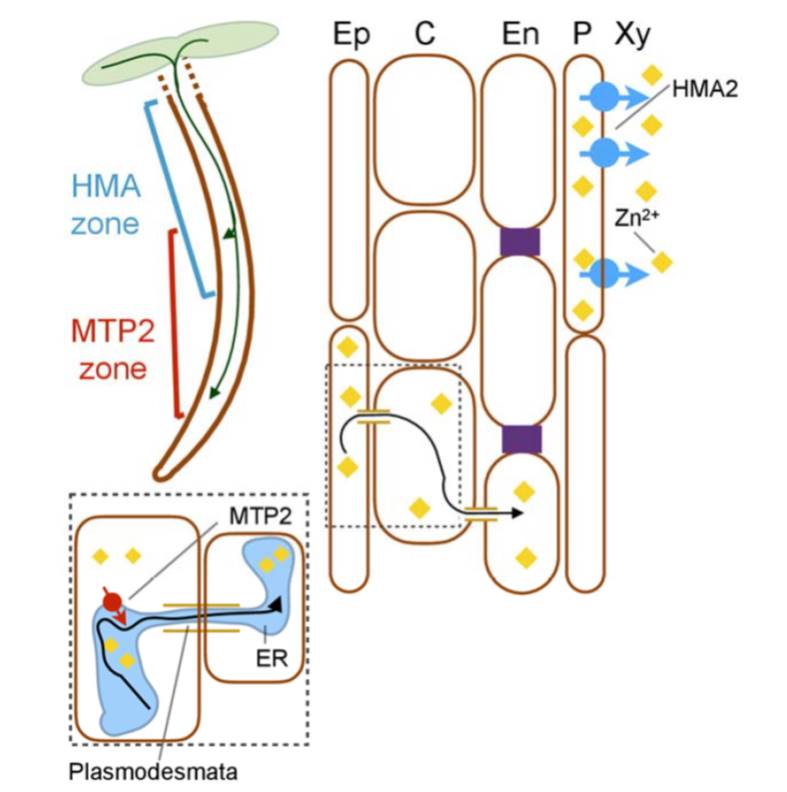
Systemic upregulation of Zn partitioning to the shoot supplements local Zn-deficiency responses (Plant Cell)
Zinc is an important micronutrient for plants and people. To better understand Zn uptake and homeostasis, Sinclair et al. used a transcriptomic approach to identify genes abnormally expressed in zinc-transporter mutants (hma2 hma4). In these mutants, Zn accumulates in roots but isn’t effectively transported…
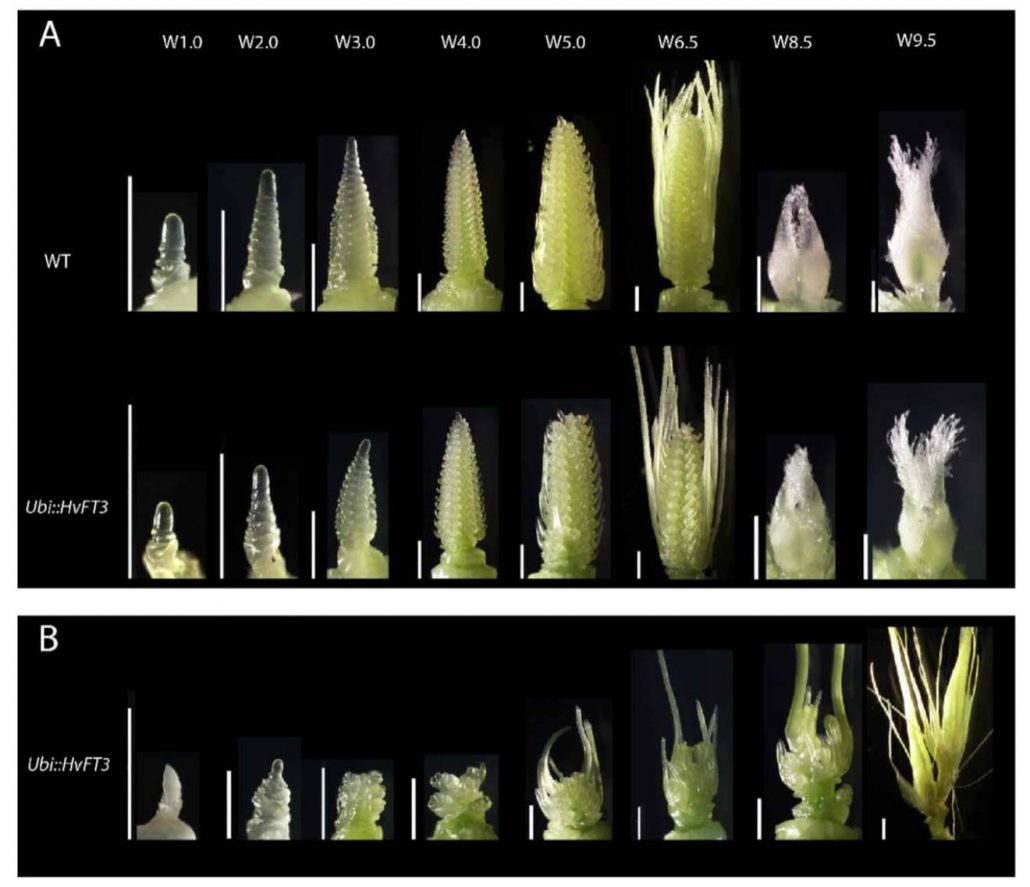

FLOWERING LOCUS T3 controls spikelet initiation but not floral development (Plant Physiol)
FT encodes a mobile protein that carries a flower-promoting signal to the shoot apical meristem. In most plants, the FT gene has duplicated and diversified. Mulki et al. investigated the function of FT3 (HvFT3) in barley. Prior work showed that overexpression of HvFT1 accellerated the initiation and…
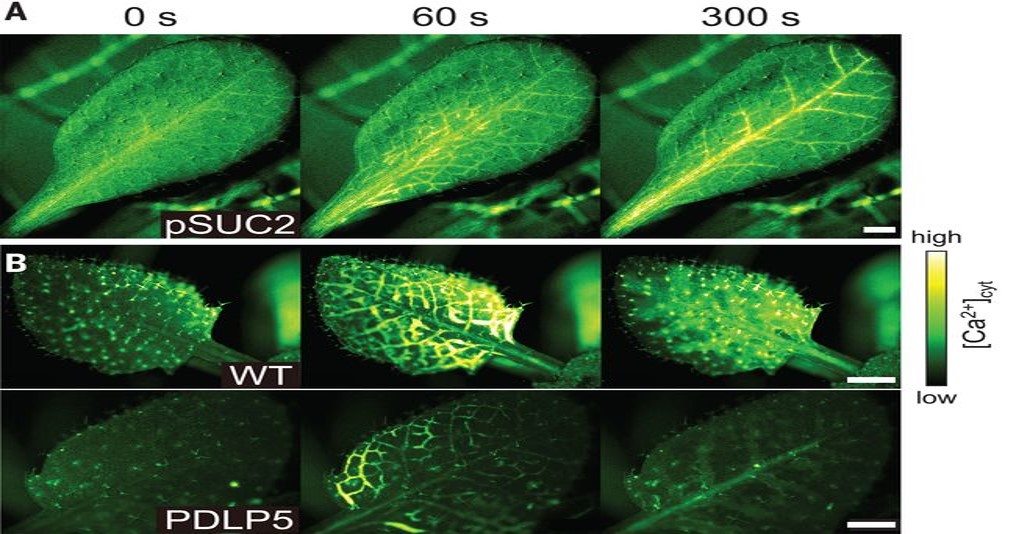
Glutamate is a wound-induced signal that activates long-distance calcium signaling (Science)
Several years of intensive research have revealed a suite of mobile signals that travel long-distances to inform meristems on developmental phase transitions or to protect distal plant tissues from abiotic or biotic stressors. In a new article published in Science, Toyota et al. (2018) identify a role…
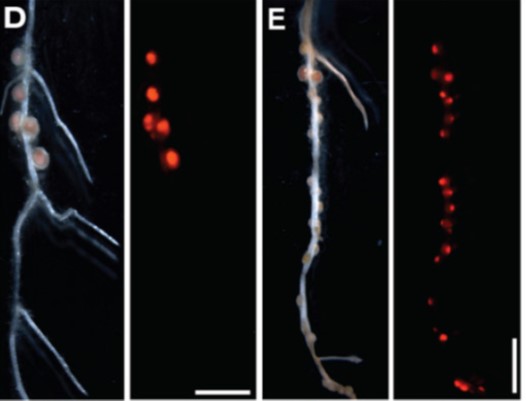
A shoot-derived miRNA ensures susceptibility to beneficial rhizobacteria in legumes (Science)
Nitrogen-fixing rhizobacteria and leguminous plants engage in a tightly controlled root symbiosis resulting from bacteria-to-plant as well as (plant) shoot-to-root communication. This interplay controls the initiation and maintenance of root nodule development while preventing the over-production of…
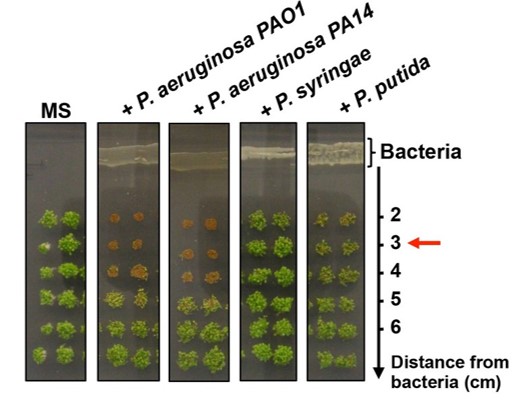
Arabidopsis seeds delay germination in the presence of pathogens (eLIFE)
The rhizosphere represents a complex and dynamic environment that poses many challenges for seed germination and seedling establishment. While a number of well-characterized abiotic factors and hormone signaling pathways are known to contribute to the initiation of seed germination, our current understanding…
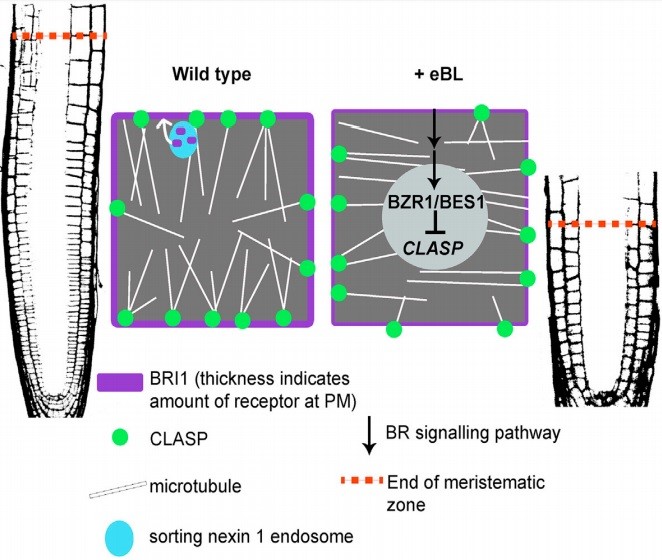
CLASP sustains cell proliferation through a brassinosteroid signaling negative feedback loop ($) (Curr. Biol.)
Brassinostreroid (BR) regulates the development of the root apical meristem. High levels of BR have inhibitory effects on cell production rates in the meristem and low levels show the opposite effect. Ruan, Halat et al. showed that BR regulates microtubule-associated CLASP (CLIP-Associated Protein) expression…
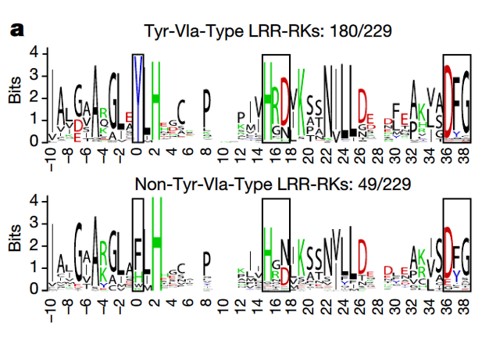
Phosphocode-dependent functional dichotomy of a common co-receptor in plant signalling (Nature)
It’s often surprising and a bit confusing when a protein that has been implicated in one process reveals itself to be involved in a totally different process as well. BAK1 (also known as SERK3) was first identified as a co-receptor for brassinosteroids (BRs), forming ligand-induced heterodimers with…
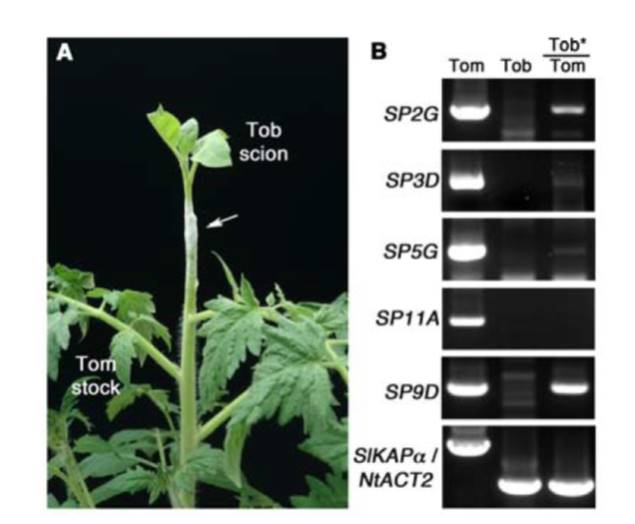
RNA Mobility and the Regulation of Flowering
In addition to hormones, proteins, and metabolites, many plants use mRNAs as mobile molecules for long-distance communication. It has been demonstrated that many mobile mRNAs are trafficked through phloem, probably by forming an RNA-protein complex to allow the stable translocation of mRNA molecules.…

