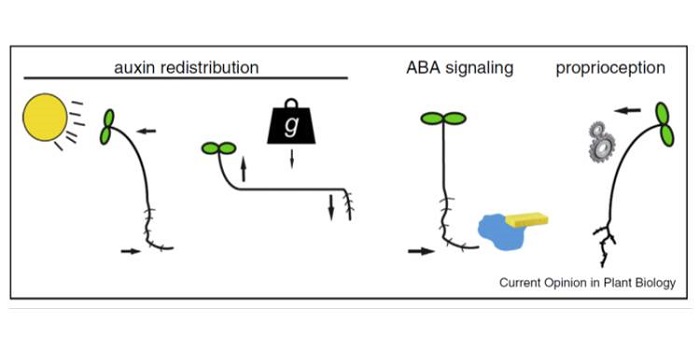
Review: Growth-mediated plant movements: hidden in plain sight ($)
Time-lapse imaging reveals the slow movements of plants, such as phototropism and gravitropism. Harmer and Brooks review the molecular bases for these growth-mediated movements. While auxin has long been known to be involved in photo- and gravitropisms, new results show that ABA is involved in the movement…
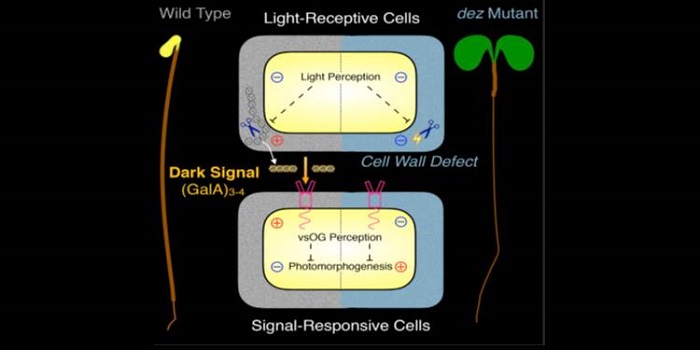
Repression of photomorphogenesis by a small cell-wall-derived dark signal ($)
Genetic screens have revealed many key components of light signaling. In this new work, Sinclair et al. provide new insights into the repression of photomorphogenesis by cell-wall derived signals. They started with a mutant, de-etiolated by zinc (dez) that shows open cotyledons and a short hypocotyl…
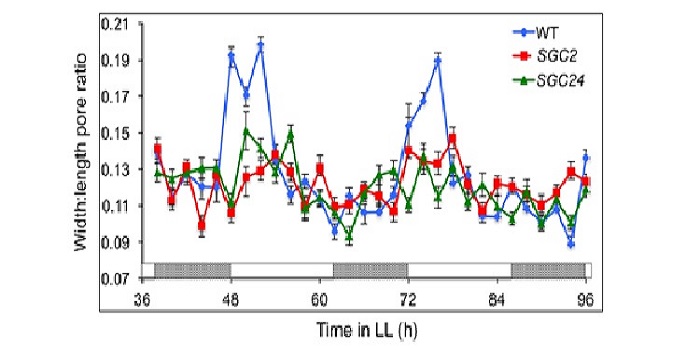
CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOICATED 1 (CCA1) and the circadian control of stomatal aperture
How do plants ‘decide’ how to respond to so many conflicting stimuli? What has the final say in stomatal aperture control? Hassidium et al. investigate the role of the oscillator gene CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOICATED 1 (CCA1) during stomatal opening and determined if CCA1 is responsive to other stimuli.…
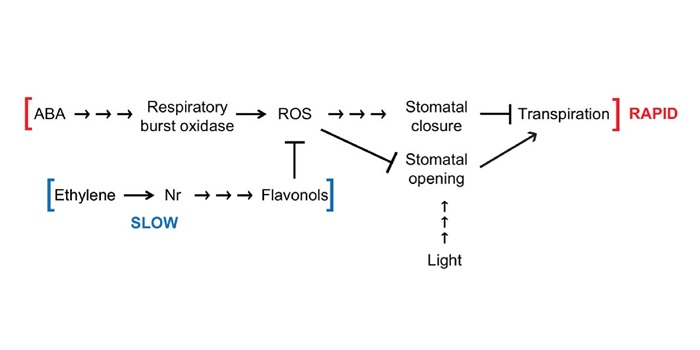
ABA-induced reactive oxygen species are modulated by flavonols to control stomata aperture
Much of our knowledge concerning ABA-induced stomatal closure comes from genetic models such as Arabidopsis and Vicia faba. Watkins et al. explore the mechanism of ROS production in this abiotic stress pathway in an important agricultural crop: tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum). Specifically, they are…
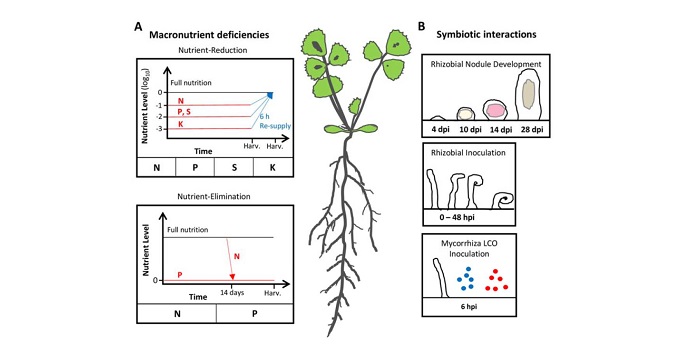
Small peptides, big importance: Small, secreted peptides as novel regulators of symbiosis and nutrient acquisition
It is becoming increasingly evident that small, secreted peptides (SSPs) are important regulators of plant development and responses to stress. Traditional gene prediction algorithms are biased toward larger coding sequences and have therefore been inadequate in the hunt for plant SSPs. To address this…
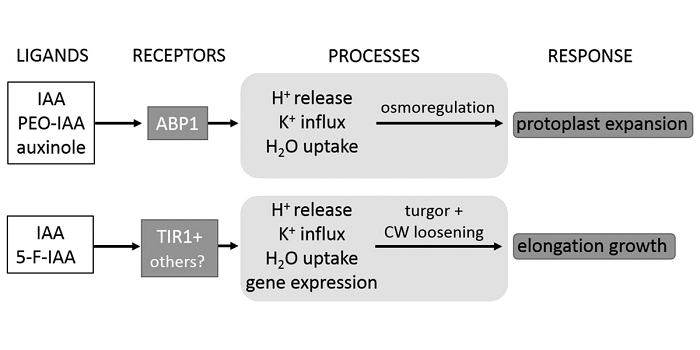
Protoplast Swelling Requires AUXIN BINDING PROTEIN1
Convincing molecular and biochemical evidence exists that members of the TRANSPORT INHIBITOR RESPONSE1/AUXIN SIGNALING F-BOX PROTEIN (TIR1/AFB) receptor family are auxin receptors that trigger auxin-induced gene expression and hypocotyl growth through enhanced expression of SMALL AUXIN UP RNA genes.…
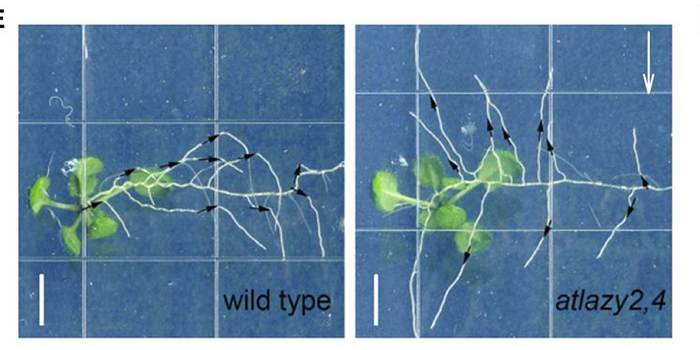
LAZY Genes Control Gravity Responses
Plant architecture is shaped by innate developmental programs as well as by adaptive responses to environmental cues. For example, the primary growth axis of shoots and roots is vertical, with lateral branches adopting some characteristic angle with respect to the main axis. If the main axis is tipped…
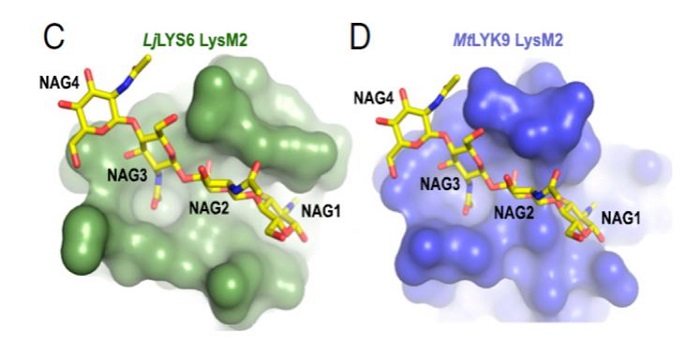
Receptor-mediated chitin perception in legume roots is functionally separable from Nod factor perception ($)
Small molecules are crucial for the recognition of friends and foes. For example, Nod factors are N-acetylglucosamine-derived “friend” signals produced by bacterial microsymbionts. Chitin is an N-acetylglucosamine-derived fungal wall polymer that plants perceive as indicating the presence of an enemy. …
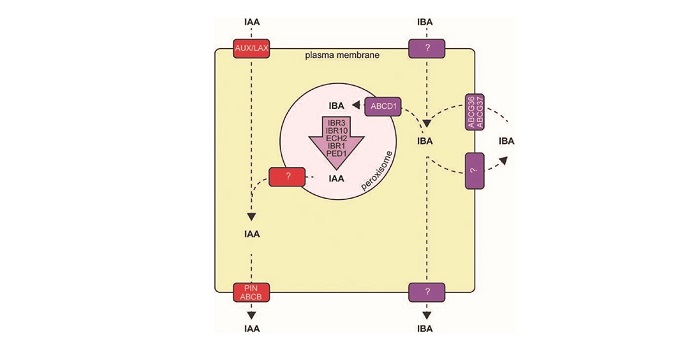
Review: Roles for IBA-derived auxin in plant development ($)
Auxin biosynthesis is a two-step process: First, tryptophan is converted to indole-3-pyruvic acid (IPyA) through the activity of the TAA1 (TRYPTOPHAN AMINOTRANSFERASE OF ARABIDOPSIS1) family of aminotransferase enzymes. IPyA is finally converted to IAA (Indole Acetic Acid) by YUCCA family of flavin…

