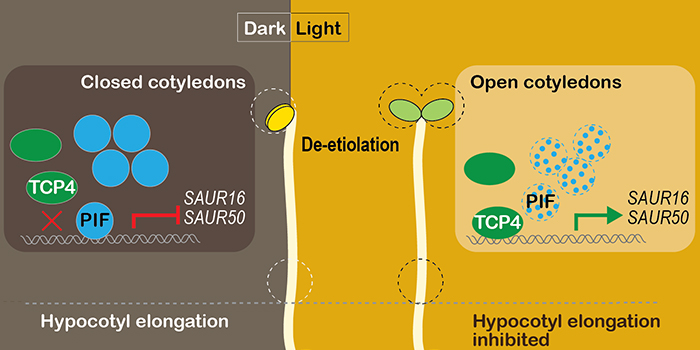
How Does Light Cause Arabidopsis Cotyledons to Open?
Dong et al. investigate cotyledon-specific light-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell (2019). https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00803
By J. Dong, N. Sun, J. Yang, Z. Deng, J. Lan, G. Qin, H. He, X. W. Deng, V. F. Irish, H. Chen, and N. Wei
Background: When germinating in darkness…
Adaptive Loss-of-Function Mutations
Xu et al. study the effects of loss-of-function mutations in over 1000 Arabidopsis accessions. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00321
By Yong-Chao Xu and Ya-Long Guo
Background: The gain of genes is thought to play important roles in the adaptation and diversification of plants. Loss-of-function…

Phloem Companion Cell-Specific Transcriptomics and Epigenomics
By conducting phloem companion cell-specific transcriptomic and epigenomic analyses, You et al. identify MRF1, a novel regulator of flowering. Plant Cell https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00714
By Yuan You1,2 and Markus Schmid1,3
1 Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, Department of Molecular…

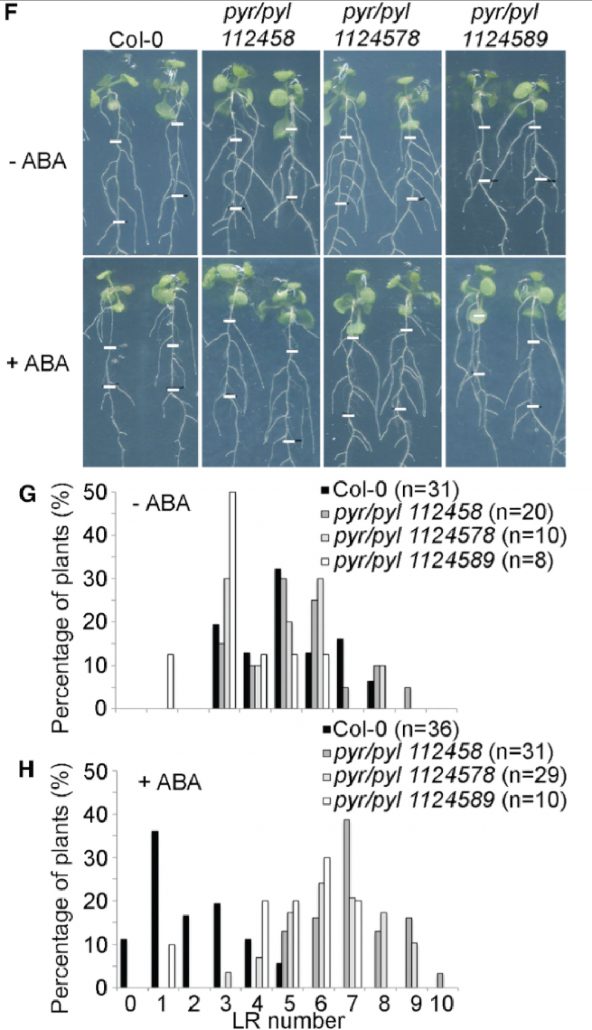
ABA Balances Plant Growth and Metabolism
Yoshida et al. investigate how the phytohormone ABA balances normal growth and metabolism. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00766.
By Takuya Yoshida and Alisdair R. Fernie, Max-Planck-Institut für Molekulare Pflanzenphysiologie.
Background: Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone that…
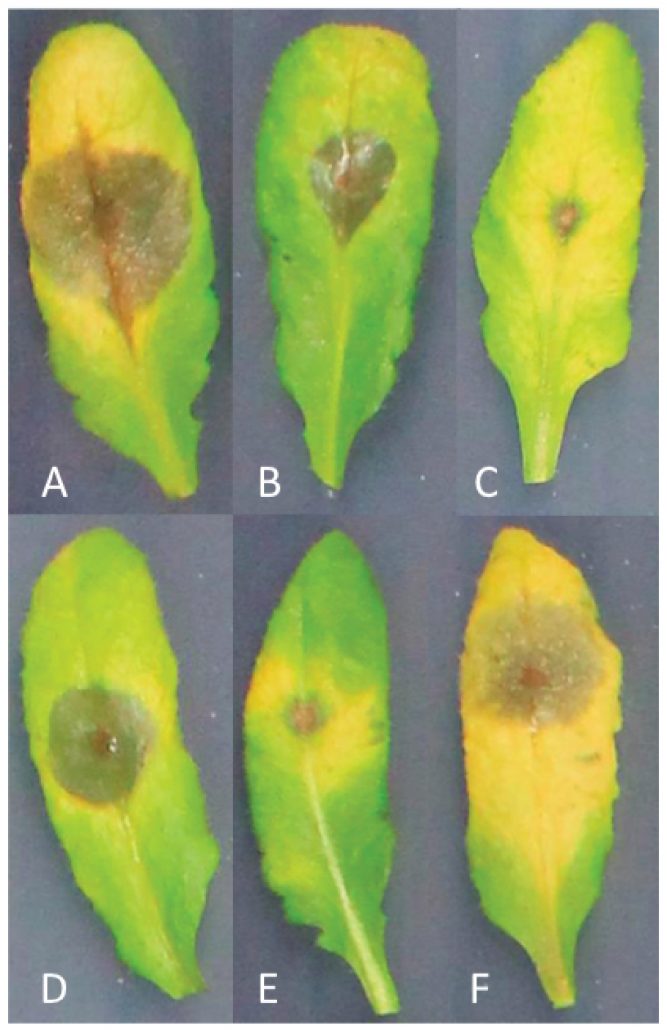

Digital imaging combined with genome-wide association mapping links loci to plant-pathogen interaction traits (Plant Phys.)
Resistance to plant pathogens is often studied as a qualitative trait than quantitative, focusing on the lesion size and pathogen numbers. However, resistance to generalist plant pathogens, such as Botrytis cinerea, is known to involve multiple genes. Fordyce et al. used high-throughput phenotyping…
The xerobranching response represses lateral root formation when roots are not in contact with water (Curr. Biol. - $)
Roots navigate through the soil, foraging for water and nutrients. Orman-Ligeza et al. observed that lateral root development is repressed when the roots are growing through the soil air spaces. Exposure to water deficit induced transcriptome reprogramming in barley roots of genes involved in many hormone…
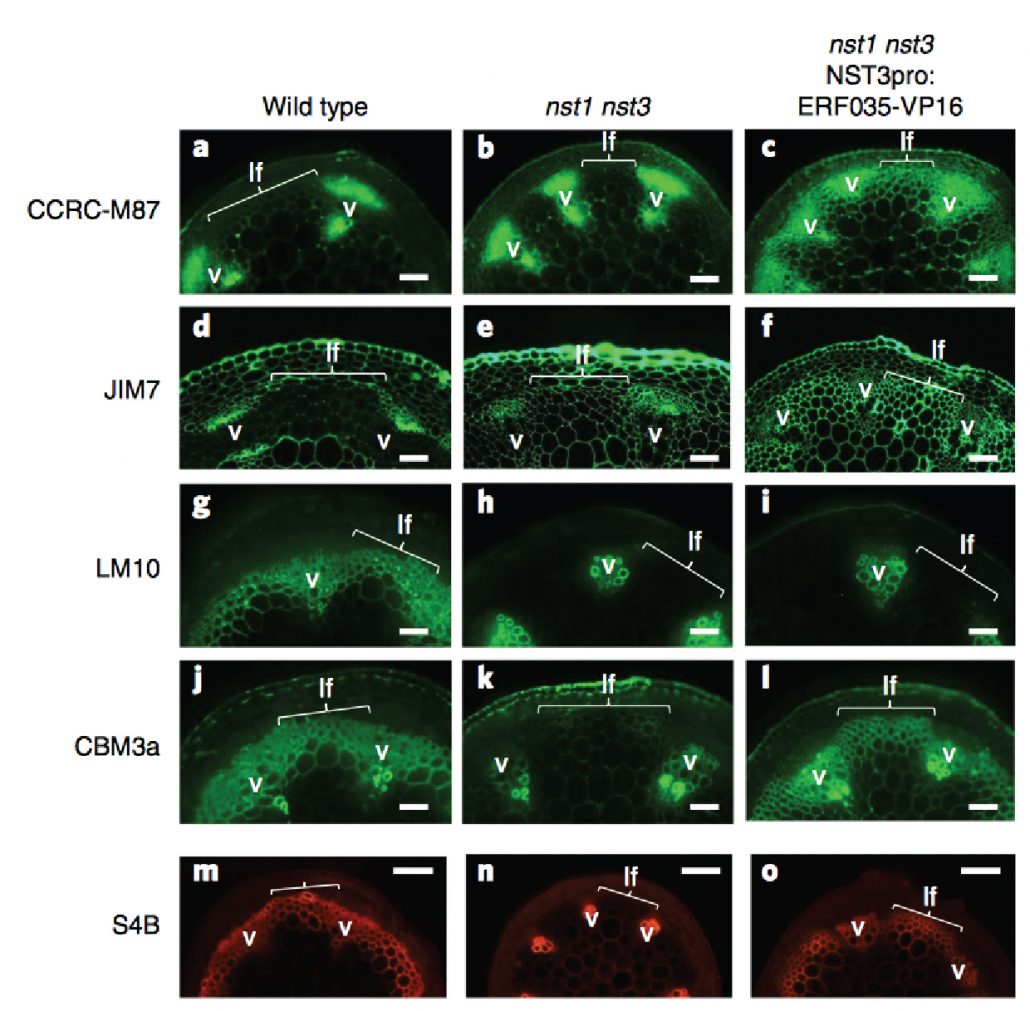
Complete substitution of a secondary cell wall with primary cell wall in Arabidopsis (Nature Plants - $)
Plant cell walls are important for terrestrial lifestyle, providing support and directing the plant growth. The primary and secondary cell walls differ in their chemical composition and flexibility. Secondary cell walls are less perceptive to industrial degradation processes and therefore pose problems…
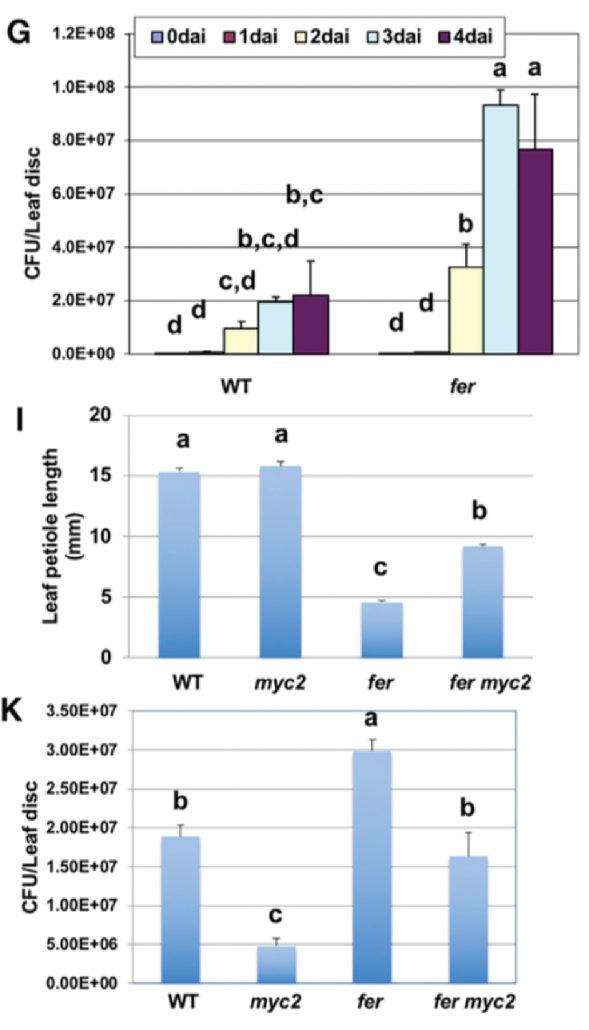
FERONIA receptor kinase contributes to plant immunity by suppressing jasmonic acid signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana (Curr. Biol. - $)
Receptor-like kinase FERONIA plays important role in the regulation of plant growth as well as interactions with the environment. In order to understand how FER affects plant growth Guo et al. examined global transcriptome changes in fer mutant. The authors observed that genes up-regulated by stress…
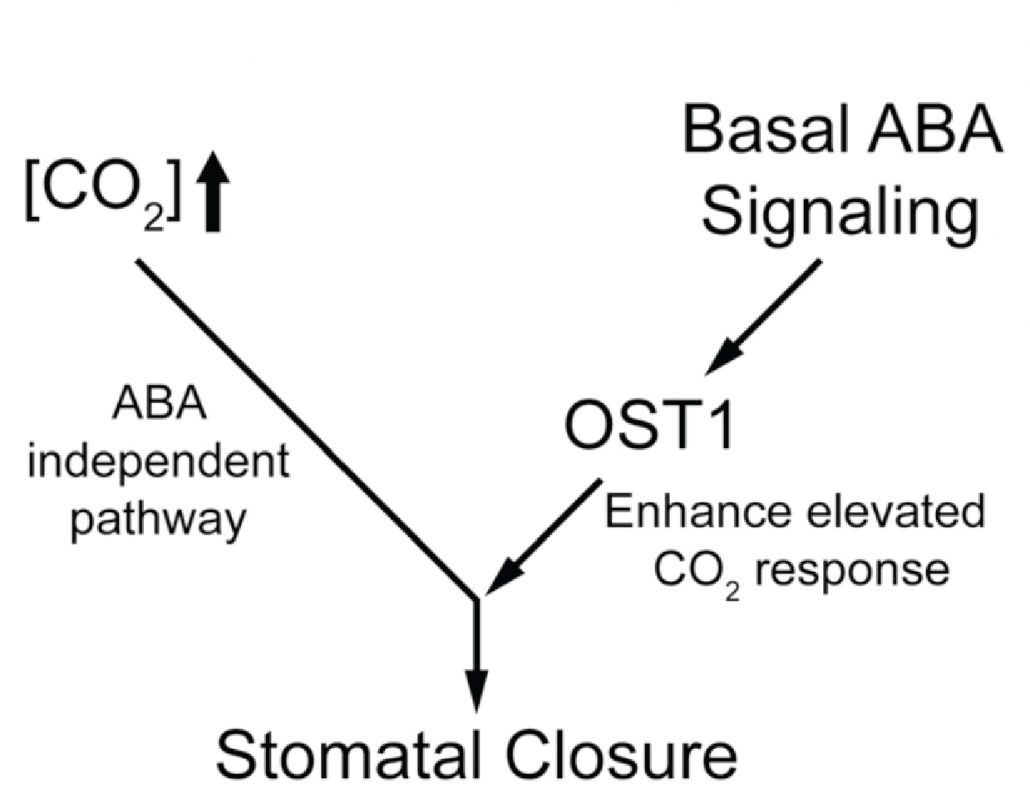
Abscisic acid-independent stomatal CO2 signal transduction pathway and convergence of CO2 and ABA signaling downstream of OST1 kinase (PNAS - $)
The global increase in CO2 concentrations results in the reduced opening of the stomata. Although reduction in the stomatal opening in response to drought relies on abscisic acid (ABA), less is known about the mechanism controlling stomatal aperture in response to elevated CO2. Hsu et al. examined stomatal…

