
Scopoletin 8-hydroxylase-mediated fraxetin production is crucial for iron mobilization (Plant Physiol)
As iron is often limiting in the environment, plants use many strategies to support iron uptake, including secretion of small molecules such as coumarins that can help to mobilize iron from the soil. Tsai et al. examined the role of a gene involved in fraxetin (7,8-dihydroxy-6-methoxycoumarin) production…

GSN1 coordinates grain number and grain size (Plant Cell)
Grain yield is determined by both grain number and grain weight. There is often a trade-off between these traits; for example, increased grain number is often associated with decreased grain weight. Using a forward-genetic approach, Guo et al. have identified a rice gene, GRAIN SIZE AND NUMBER1 (GSN1)…

Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors ensure formation of one functional megaspore per ovule (PLOS Genet)
Usually the female germline starts with one MMC (megaspore mother cell) per ovule that becomes four megaspores through the process of meiosis. Out of these four, only one survives to produce a functional megaspore (FM); the other three undergo a degeneration process. The FM forms the embryo sac. In this…

An SPX-RLI1 module regulates leaf inclination in response to phosphate availability in rice (Plant Cell)
The angle at which a rice leaf bends affects its ability to intercept light and also the density at which the plants can be sown. Previous work has shown that brassinosteroid hormones and the BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1 (BU1) gene affect leaf angle. Ruan, Guo, Xu et al. investigated the role of phosphate…

Review: The root transition zone: A hot spot for signal crosstalk (TIPS) ($)
Plant roots are an excellent system to study the interactions between endogenous (phytohormones) and exogenous (abiotic stresses) stimuli. The root can be considered as three sections: the meristematic zone (where active cell division occurs), the transition zone (acting as a boundary between meristem…
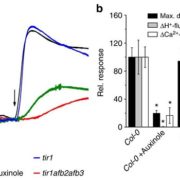
AUX1-mediated root hair auxin influx governs SCFTIR1/AFB-type Ca2+ signaling (Nature Comms)
The phytohormone auxin is transported in a polar fashion through PINs (PIN-FORMED) and PGPs (P–GLYCOPROTEIN) as auxin efflux carriers and AUX1 and LAXs (LIKE-AUX1) as influx carriers. Previous experiments from oat coleoptiles and corn root hairs indicate that one of quickest auxin responses is cell…
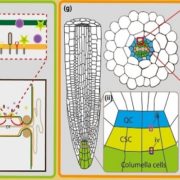
Viewpoint: Cell-cell junctions: What’s their function? (New Phytol)
Plasmodesmata are contiguous cell-cell junctions that provide an avenue for intracellular (symplastic) communication between neighboring plant cells. In recent years, researchers have unravelled key aspects of plasmodesmata development and function in cell-cell signalling during a multitude of responses…
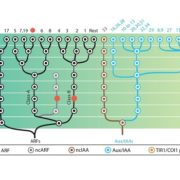
Deep evolutionary roots for the plant hormone auxin (eLIFE)
Auxin is an endogenous plant hormone that orchestrates complex tissue development across diverse green plant lineages. In a recent article, Mutte et al. performed a deep phylogenomics analysis of known and predicted auxin signalling mechanisms present in green plants and their algal predecessors. This…
What We're Reading: April 6th
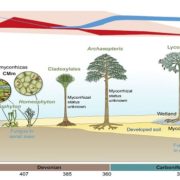
Review: The origin and evolution of mycorrhizal symbioses
Many fungi are pathogens that kill or weaken their plant hosts. However, there are also many species that form beneficial relationships with plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. One of these mutualisms is the mycorrhizal association between a…

