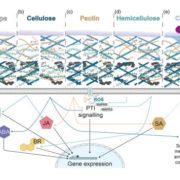
Review. Plant cell wall-mediated immunity: cell wall changes trigger disease resistance responses
Plant cell walls have recently been revealed as an essential factor of plant environment monitoring system, much more than just a passive defensive barrier as previously thought. In a recent work, Bacete et al. have reviewed how changes to plant cell wall integrity affect disease resistance. More specifically,…
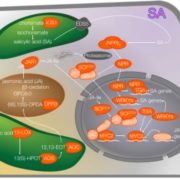
Jasmonic acid and salicylic acid signaling in fern Azolla filiculoides and its cyanobiont
The phytohormones jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA) play key roles in how plants respond to microbes. However, this interplay between JA, SA and microbes is less understood in non-angiosperm linages. de Vries and colleagues examine JA/SA signalling between the water fern Azolla filiculoides…
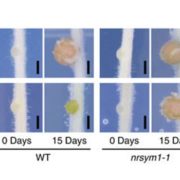
A NIN-LIKE PROTEIN mediates nitrate-induced control of root nodule symbiosis in Lotus japonicus
Legumes form root endosymbioses with Rhizobium bacteria in a special structure called nodule. In this symbiotic relationship, on one hand the plant provides the microbe with sugars and in exchange it receives fixed atmospheric nitrogen, the main limiting element for plant growth. Nevertheless, when nitrogen…
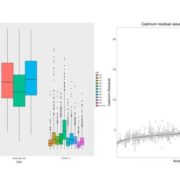
Genomewide association study of ionomic traits on diverse soybean populations from germplasm collections
Germplasm collections are invaluable resources for plant science and the elemental content of the seeds is a strong indication of the plant’s response to its specific environment. In this study, Ziegler et al. have selected 1,653 soybean accessions from the USDA Soybean Germplasm Collection and seeds…
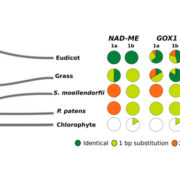
Ancient duons may underpin spatial patterning of gene expression in C4 leaves
C4 photosynthesis describes a biochemical CO2-concentrating mechanism that relies on the spatial separation of biochemistry between two cell types, mesophyll cells (MCs) and bundle sheath cells (BSCs). However, there is currently little evidence on how some genes are preferentially expressed in BSCs…
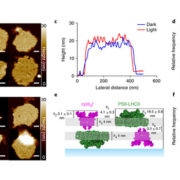
Dynamic thylakoid stacking regulates the balance between linear and cyclic photosynthetic electron transfer
The activation of photosynthetic electron transport upon a dark-to-light transition occurs prior to the initiation of CO2 fixation by Rubisco in the Calvin cycle. A mechanism known as cyclic electron transfer (CET) exists that generates the proton motive force required to drive ATP synthesis without…

Ethylene signaling modulates cortical microtubule reassembly in response to salt stress
Ethylene is an important mediator during plant adaptation to salt stress. During salt stress, ethylene has been shown to promote microtubule (MT) stability and organization. Dou et al. further examine this pathway using Ag+ to block ethylene signaling in addition to using various mutants. In wildtype…
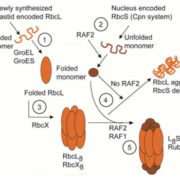
RAF2 is a Rubisco Assembly Factor in Arabidopsis thaliana
The assembly of the carbon fixing enzyme Rubisco is a complex process and involves many chaperones including RAF1, RbcX and the chaperonins. Recent evidence pointed to the existence of another chaperone, RAF2, conserved among photosynthetic organisms. The protein has similarity to pterin-4α-carbinolamine…
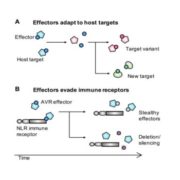
Review. The coming of age of EvoMPMI: evolutionary molecular plant-microbe interactions across multiple timescales
Often, a wide gap exists between evolutionary research, that is focused on theoretical approaches and organism evolution across multiple timescales, and molecular research aspiring to solve mechanistic puzzles of how particular systems work. Plant Biology is no exception to this, and much can be learnt…

