
Laccase Confers Biotic Stress Tolerance in Cotton
Cotton (Gossypium spp.) is a globally cultivated globally crop of vast economic importance. Pathogens and pests are major limitations to cotton yield and quality. Verticillium wilt, caused by the fungus Verticillium dahliae, is the disease most detrimental to cotton production. Cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa…
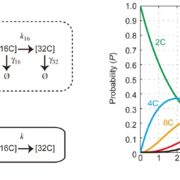
Probing the stochastic property of endoreduplication in cell size determination of Arabidopsis thaliana leaf epidermal tissue
PLOS One. Endoreduplicated cells grow in size as their DNA content increases. The distribution of size was observed to be Poisson. This allowed the authors to create a mathematical model with a single parameter which describes the probability of exiting endoreduplication. The model recovers cell size…
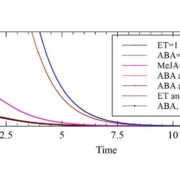
A mathematical model of the interaction of abscisic acid, ethylene and methyl jasmonate on stomatal closure in plants
PLOS One. Plant stomatal opening is controlled by phytohormones, among other factors. This article models the phytohormone signaling response in guard cells using ordinary differential equations (ODEs). Sixteen components in this system were analyzed by constructing 16 different models and determining…
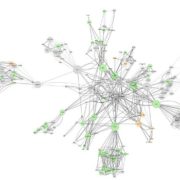
Predicting gene regulatory networks by combining spatial and temporal gene expression data in Arabidopsis root stem cells
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. GENIST (gene regulatory network inference from spatiotemporal data) is a new algorithm developed by de Luis Balaguer et al to predict new gene interactions and transcriptional regulators (available at https://github.com/madeluis/GENIST). The algorithm combines inference of…
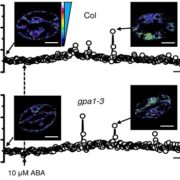
A new discrete dynamic model of ABA-induced stomatal closure predicts key feedback loops
PLOS Biol. This article describes a stochastic mathematical model of the stomatal closure network responding to abscisic acid (ABA). The Boolean network is constructed from a comprehensive literature review of the components’ dependencies. The model’s predictions agree with experimental data 90%…
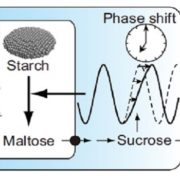
Adjustment of the Arabidopsis circadian oscillator by sugar signalling dictates the regulation of starch metabolism
Sci Reports. Both starch degradation and accumulating sucrose levels are related to the circadian cycle, although it is unknown which is the primary regulator. The authors created a mathematical model wherein the circadian oscillator responds to sucrose. The model predictions were experimentally validated…
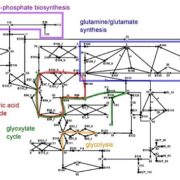
Modeling the metabolism of Arabidopsis thaliana: Application of network decomposition and network reduction in the context of Petri nets
Front. Genetics. In this paper, the authors model the metabolism in Arabidopsis using Petri nets (PN). PNs are dynamic models that use “tokens” to represent movement between the places and edges of the model, representing the products of a reaction. The model was simplified using reduction techniques,…
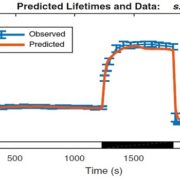
Dissecting and modeling zeaxanthin- and lutein-dependent nonphotochemical quenching in Arabidopsis thaliana
Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. Xanthophylls zeaxanthin and lutein are involved in the nonphotochemical quenching (NPQ) pathway which is triggered in response to excess photons. The roles of zeaxanthin and lutein in NPQ are studied using mathematical models and Arabidopsis mutants. The authors hope that future…

What We're Reading: January 19th
This week's papers were seleted by Renee Dale. Renee is a PhD student in biology and an MS student in statistics at Loiusiana State University who is studying mathematical biology and biostatistics for plant biology applications. She is also working on an educational video game!
Renee selected these…

