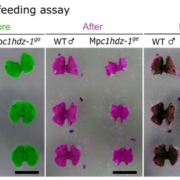
How Marchantia polymorpha avoids bug bites (bioRxiv)
Plants took hundreds of million years to evolve from aquatic to land environments. Biotic and abiotic stress adaptation contributed to the transition. In this preprint, Romani et al. elucidated functions of the transcription factor CLASS I HOMEODOMAIN LEUCINE-ZIPPER (C1HDZ) in the early land plant Marchantia…

A feedforward loop controls vascular regeneration and tissue repair through local auxin biosynthesis (Plant Cell)
Plant cells are entrapped in rigid cell walls, so morphogenesis relies on asymmetric cell division (ACD) and positional cues to regulate tissue patterning. The Arabidopsis phloem is a good system to study tissue patterning due to its relatively simple composition: sieve elements (SEs) and companion cells…
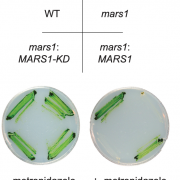
Mars1 kinase signaling in the chloroplast unfolded protein response (eLIFE)
In stressful situations, such as high light and nutrient scarcity, the chloroplast may experience increased proteotoxicity due to a surge in damaging reactive oxygen species. In response, a signal is sent to the nucleus to increase production of many proteins, including proteases and chaperones to help…

The cis-regulatory codes of response to combined heat and drought stress (bioRxiv)
As sessile organisms, plants must not only respond to a single stress, but multiple stresses at the same time. To understand the DNA regulatory elements that mediate the transcriptional response to heat, drought and combined heat and drought stress, Azodi et al. utilized the known transcription factor…
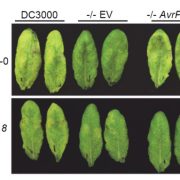
A plant kinase exploited by a bacterial effector (bioRxiv)
Pathogens have evolved a suite of effector proteins that are secreted into plants and aid successful colonization. AvrPtoB is a well-conserved effector of pathogenic Pseudomonas syringae strains that targets multiple plant defense-related proteins and is required for pathogen virulence and bacterial…
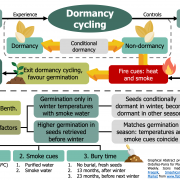
Evidence for physiological seed dormancy cycling in the woody shrub Asterolasia buxifolia and its ecological significance in fire‐prone systems ($) (Plant Biol.)
Physiologically dormant seeds shift between dormancy (i.e., unable to germinate), conditional dormancy (i.e., germination restricted to a narrow set of conditions), and non-dormancy (i.e., germination under a wide range of conditions) in response to environmental changes. This mechanism –known as dormancy…

Update: How plants sense and respond to stressful environments (Plant Phys)
A longstanding question in plant science is how plants “know” that they are under threat. The identification of cell-surface receptors that identify conserved pathogen patterns sheds some light on biotic stress perception, but what about abiotic stresses such as excessive heat or drought? Lamers…

Perspective: Multiscale computational models for crop improvement (Plant J)
Throughout the plant science community, the use of computational or in silico analyses which precede traditional studies are gaining traction to identify research opportunities. Multiscale computational models are those which assimilate data from all biological system levels from gene to ecosystem. Benes…
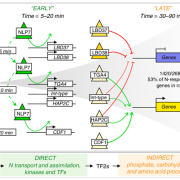
Transient genome-wide interactions of the master transcription factor NLP7 initiate a rapid nitrogen-response cascade (Nature Comms.)
Transcription factors (TFs) and their genome-wide targets form gene regulatory networks that allow organisms to respond to stimuli. However, conventional biochemical assays only identify a subset of the TF-target interactions. In this paper, Alvarez et al. elucidate the genetic network of NIN-LIKE PROTEIN…

