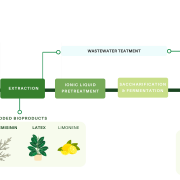
Accumulation of high value bioproducts in planta can improve the economics of advanced biofuels (PNAS)
Biofuels can be obtained from bioenergy crops such as sorghum, maize and sugarcane. However, the production of bioethanol is still more expensive than that of petroleum. Given the importance of replacing conventional fossil fuels with renewable liquid fuels, the biorefinery system should be improved…
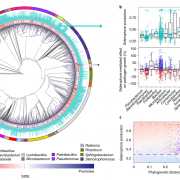
Rhizosphere microbiome protects plants from a pathogen via iron competition (Nature Microbiol)
Iron is an essential element for most living organisms, including plant-associated bacteria. As iron is insoluble in most soils, many soil-borne bacteria scavenge iron using siderophores, a chemically diverse group of secondary metabolites with a high affinity for iron. Siderophores are known to drive…
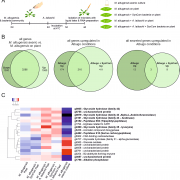
Fungal antagonism of Arabidopsis oomycete infection requires a previously uncharacterized secreted hydrolase (bioRxiv)
Antagonist interactions between microbes of the phyllosphere stabilize the microbiome and some “hub” organisms can exert strong effects on community structure. The yeast family Ustilaginales contains several apathogenic species that are microbial antagonists that can inhibit infection from diverse…
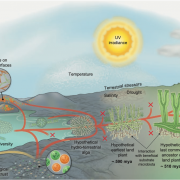
Review: Evo-physio: on stress responses and the earliest land plants (J. Exp. Bot.)
Streptophytes are a grade of mostly freshwater algae that transitioned into land, a singularity that in turn gave rise to all present terrestrial flora. This passage along the hydrological gradient that culminated in land habitation required key adaptations to overcome previously unencountered terrestrial…
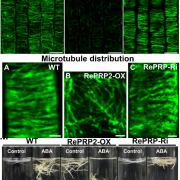
“Order by disorder”- intrinsically disordered proteins (Plant Physiol.)
Intrinsically disordered proteins (IDP) have repetitive protein sequences but lack a defined 3D structure and are deployed to do some challenging functions that a protein with a defined 3D structure cannot perform. One such IDP, Oryza sativa REPETITIVE PROLINE-RICH PROTEIN (OsRePRP) is involved in inhibiting…
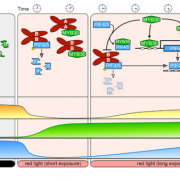
MYB30 negatively regulates photomorphogenesis by interacting with PIFs and phytochromes in Arabidopsis (Plant Cell)
Photomorphogenesis is the growth and development of plants in response to light. The phytochrome family of photoreceptors absorbs red and far-red light, and in Arabidopsis the most abundant phytochromes are phyA and phyB. PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTORS (PIFs) repress photomorphogenesis, and under red…
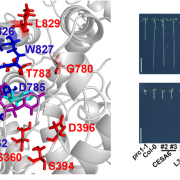
Endosidin20 targets the cellulose synthase catalytic domain to inhibit cellulose biosynthesis (Plant Cell)
Cellulose is an indispensable component of plant cell wall formation. Cellulose is synthesized at the plasma membrane by a cellulose synthase complex (CSC) made up of at least 18 monomeric cellulose synthases (CESAs). In this study, Huang et al. used a chemical genetic approach to explore the structure…

Mutations PETALOSA cause a dominant double-flower phenotype (J. Exp. Bot.)
Flower development has always been a fascinating field of research in plant biology. While molecular studies in the past focused on regulatory genes involved in the formation of floral organs in model species, current investigations are addressing the genetic determinants underlying the huge variety…
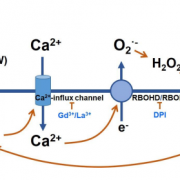
Hydrogen mediates tolerance to cadmium-induced root toxicity (Plant Physiol.)
Heavy metals are a potential threat to human health, especially in areas with high industrial activity where the metals leach in the soil to contaminate underground water. These metals are a threat to plants too, resulting in stunted growth and their eventual death. Wu et al. carried out a mechanistic…

