
Dynamics of Xylem Water Release
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe water transport system of woody plants can experience periods of excessive xylem tension. It is generally assumed that during these times, water stored in capacitive tissue moves into the transpiration stream and buffers the liquid tensions that develop inside the vessel lumen, thereby protecting…
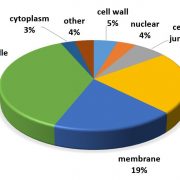
Plasmodesmatal Structure and Function
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThree types of phloem loading have been defined in plants: 1.) “active apoplasmic” loading, in which sugar transporters are responsible for the active uptake of sugars into the sieve element companion cell complex (SECCC) which is believed to be symplasmically isolated; 2.) “passive symplasmic”…
The Unfolded Protein Response and Plant Development
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe unfolded protein response (UPR) is a cellular stress response involving the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The UPR is activated in response to an accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins in the lumen of the ER. However, ER stress can also be induced in the absence of external stressors,…
Identification of Leaf ER Bodies in Arabidopsis
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideEndoplasmic reticulum bodies (ER bodies) are endoplasmic reticulum-derived organelles specific to the order Brassicales that are thought to play a role in plant defense against biotic factors. ER bodies are generally classified into two types: 1.) constitutive ER bodies that are found in the epidermal…

Phosphate Starvation Alters Root Calcium Signatures
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsidePlant roots foraging in the soil have to sense, transduce, and respond to fluctuations in water and nutrients plus a multitude of stresses to which they may be subjected. Biotic and abiotic stresses (including mechanical, salt, osmotic, and oxidative stress) trigger rapid and transient modulations in…
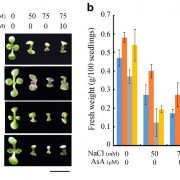
Ethylene and ABA Regulate Ascorbic Acid and Reactive Oxygen Species
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideThe phytohormones ethylene and abscisic acid (ABA) often interact in controlling plant growth and development processes as well as plant responses to stress. The detailed mechanisms underlying the interaction of these two phytohormones, which may act synergistically or antagonistically with each other,…
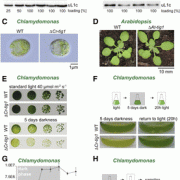
The Role of Trigger Factor in Chloroplasts
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideChloroplasts contain a small genome that encodes only a minor fraction of approximately 60 to 100 proteins of the entire 3,000 proteins localized in the chloroplast. Chloroplast-encoded proteins, however, are major subunits of important protein complexes involved in gene expression and photosynthesis.…

A Calcium Sensor Involved in Salt Tolerance
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideIt is estimated that 20% of irrigated land is negatively impacted by salt and 1% to 2% of irrigated land is lost each year due to the accumulation of salt. Salt, particularly sodium chloride (NaCl), negatively affects plant growth in several ways. The accumulation of salt in the soil restricts water…
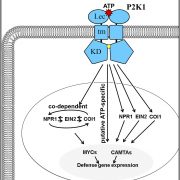
Extracellular ATP-Induced Transcriptome
Plant Physiology, Plant Physiology: On The InsideTransmembrane receptors monitor changes in extracellular ATP concentration in order to detect either the uncontrolled ATP release caused by the necrosis of nearby cells or to instigate active ATP release following pathogen detection. Extracellular ATP can be perceived, therefore, as a sign of damaged…

