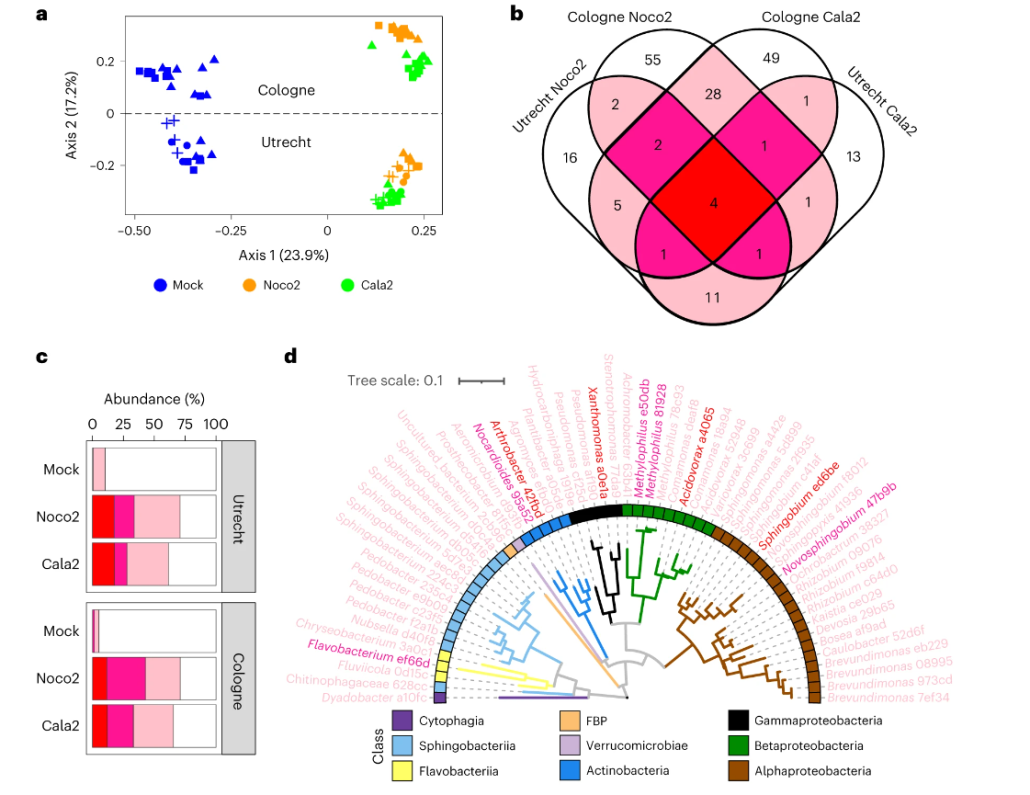
An opportunistic plant pathogen disrupts leaf microbiome through secretion of plant cell wall degrading enzymes
Healthy plants possess a functional immune system, and their leaves harbor a structured microbial community, including opportunistic pathogens. These opportunistic pathogens can trigger plant diseases under conducive conditions, such as when plant immunity is compromised, and the microbial community…
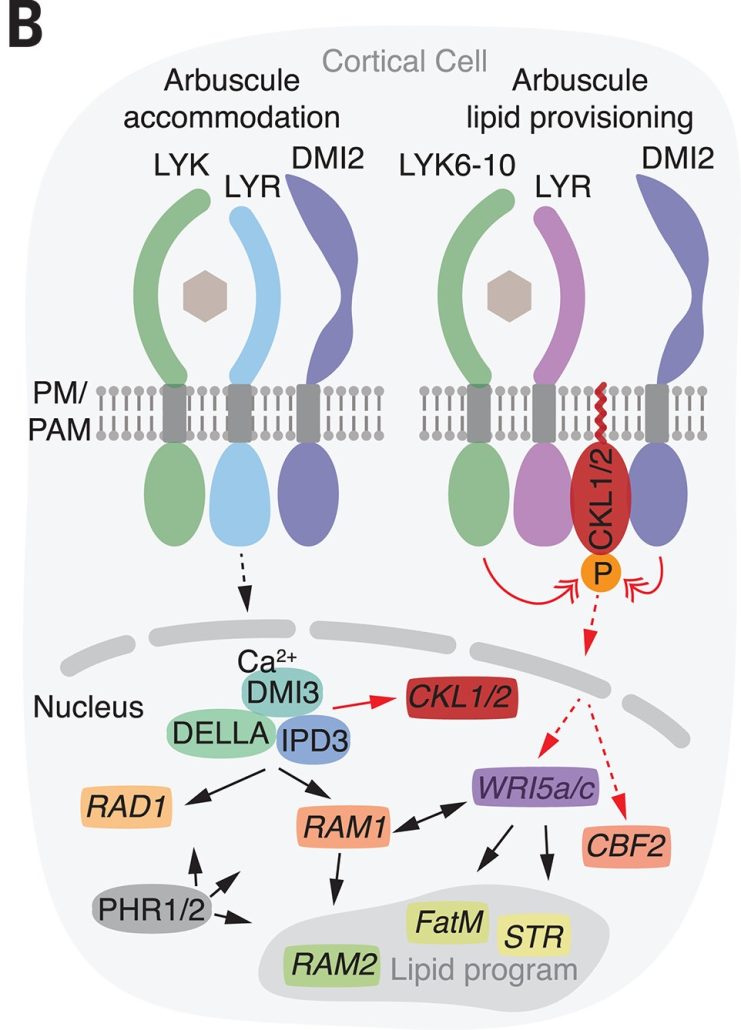
Receptor-associated kinases control lipid provisioning in plant–fungal symbiosis
Most plants benefit from symbiotic associations with fungi, in which the fungi aid in nutrient update particularly of phosphate, and the plant returns the favor by supplying the fungi with lipids. Several but not all of the molecular players required for these important pathways have been identified.…
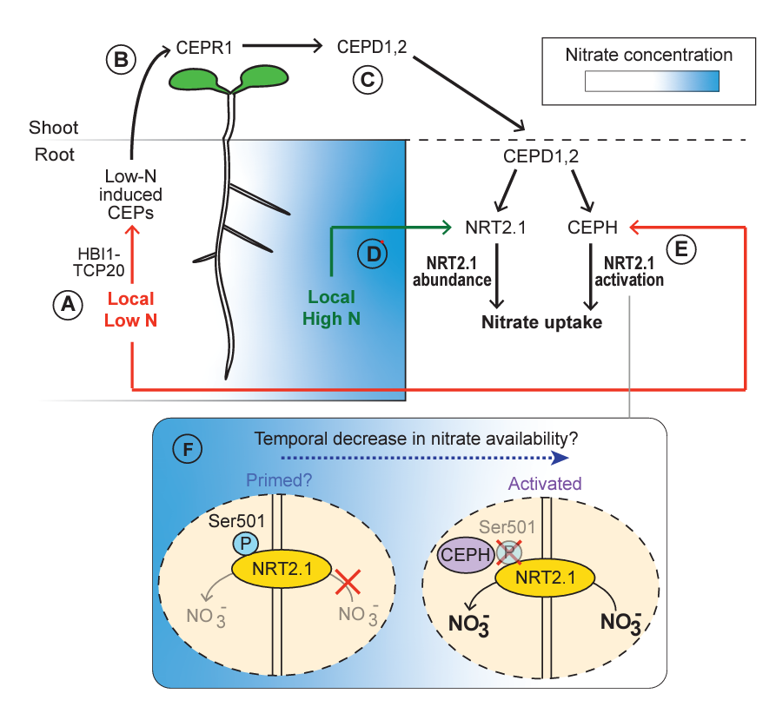
Review: CEP hormones at the nexus of nutrient acquisition and allocation, root development, and plant–microbe interactions
C-TERMINALLY ENCODED PEPTIDE (CEP) is a multigene family of peptide hormones originally described as systemic long-distance signals in response to nitrogen limitation. Over the years since the discovery of these peptide hormones, the literature on CEP biology has expanded the repertoire of developmental…
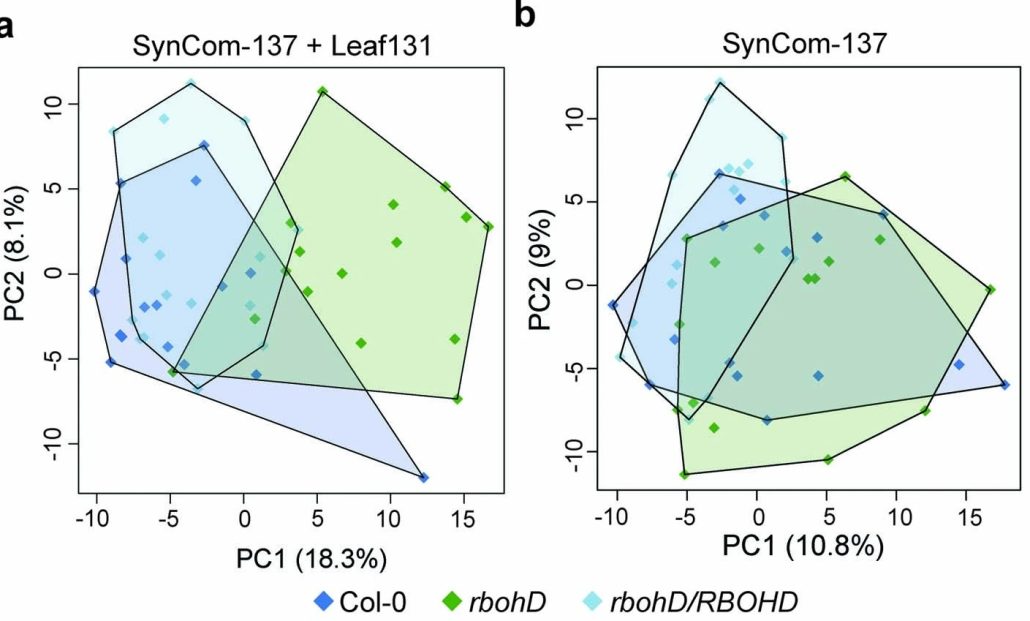
Shooting yourself in the foot: Obligate biotrophic pathogen induces protective microbiome in Arabidopsis
Obligate plant pathogens cannot survive without their host plant. Therefore, understanding how the plant and its microbiome respond to the obligate biotrophs has real challenges in making sure that the response that is being monitored is not an artifact of the experimental step up. A recent study by…
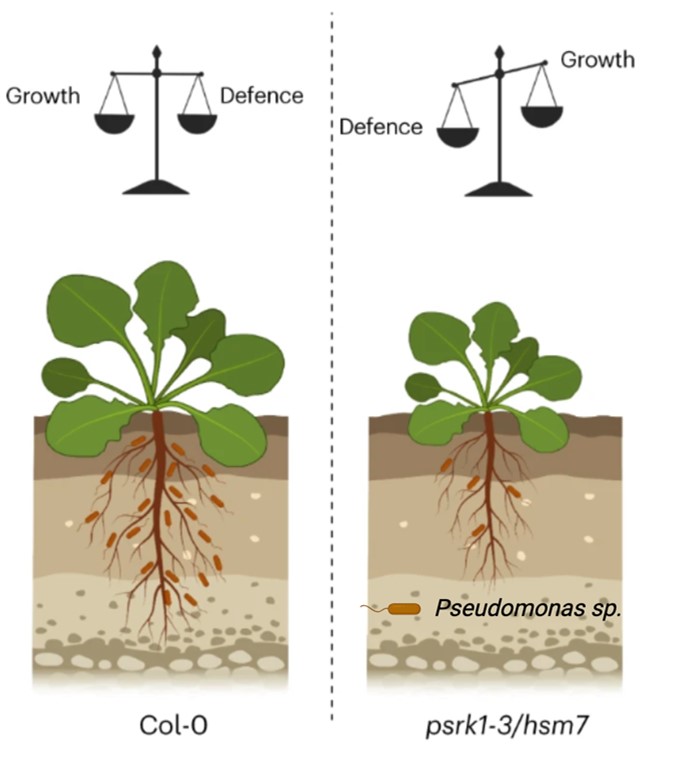
PSKR1 balances the plant growth–defence trade-off in the rhizosphere microbiome
Plants are colonized by numerous beneficial microorganisms in the rhizosphere, including Pseudomonas fluorescens, that provide benefits including nutrient acquisition and pathogen protection. Host plants must tune their immune systems to restrict microbial overgrowth, while avoiding overstimulation of…
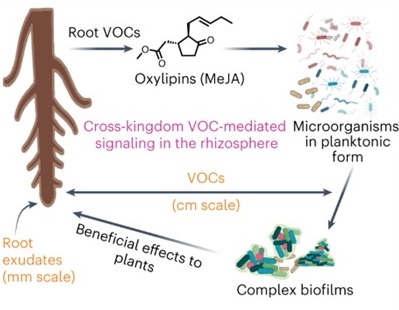
Volatile methyl jasmonate from roots triggers host-beneficial soil microbiome biofilms
Volatile molecules released from plant roots (root VOCs, rVOCs) can diffuse over long distances, thereby increasing the sphere of plant influence. However, their influence on complex soil microbial communities (or microbiomes) and ecological implications are poorly understood, mainly due to technical…
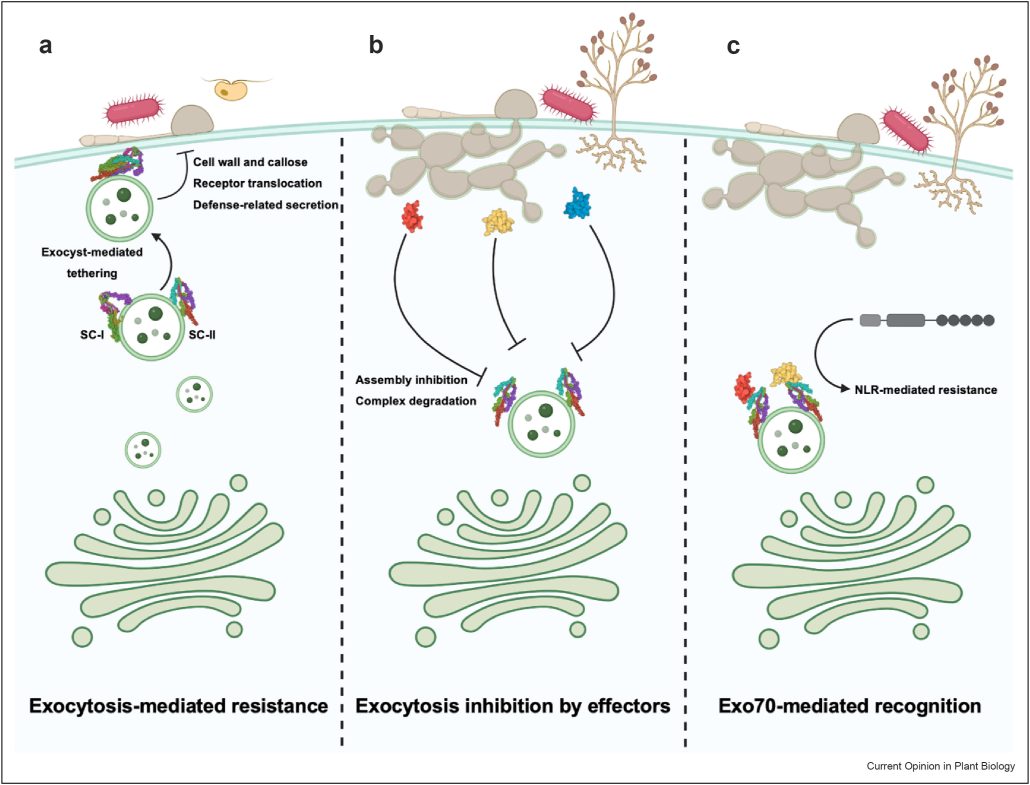
Review: The exocyst complex is targeted by pathogen effectors
The exocyst complex is a conserved octameric protein complex in eukaryotic cells. Its primary function is to tether secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane during the exocytosis process, and it is also involved in autophagy and host-pathogen interactions. Intriguingly, EXO70, one of the subunits of…
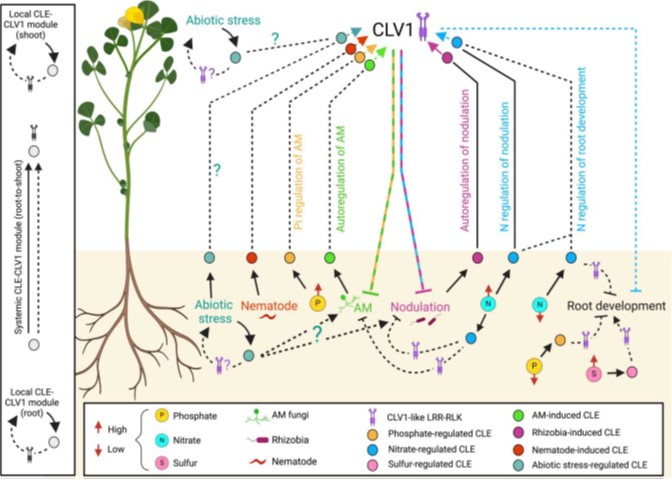
Review: CLAVATA signaling in plant-environment interactions
CLAVATA 3/EMBRYO SURROUNDING REGION-related (CLE) peptides and CLAVATA type receptors have been well charecterized for their role in root and shoot apical meristem maintenance in Arabidopsis. CLE peptides are also referred to as “peptide hormones” for their role in contolling physiological and developmental…
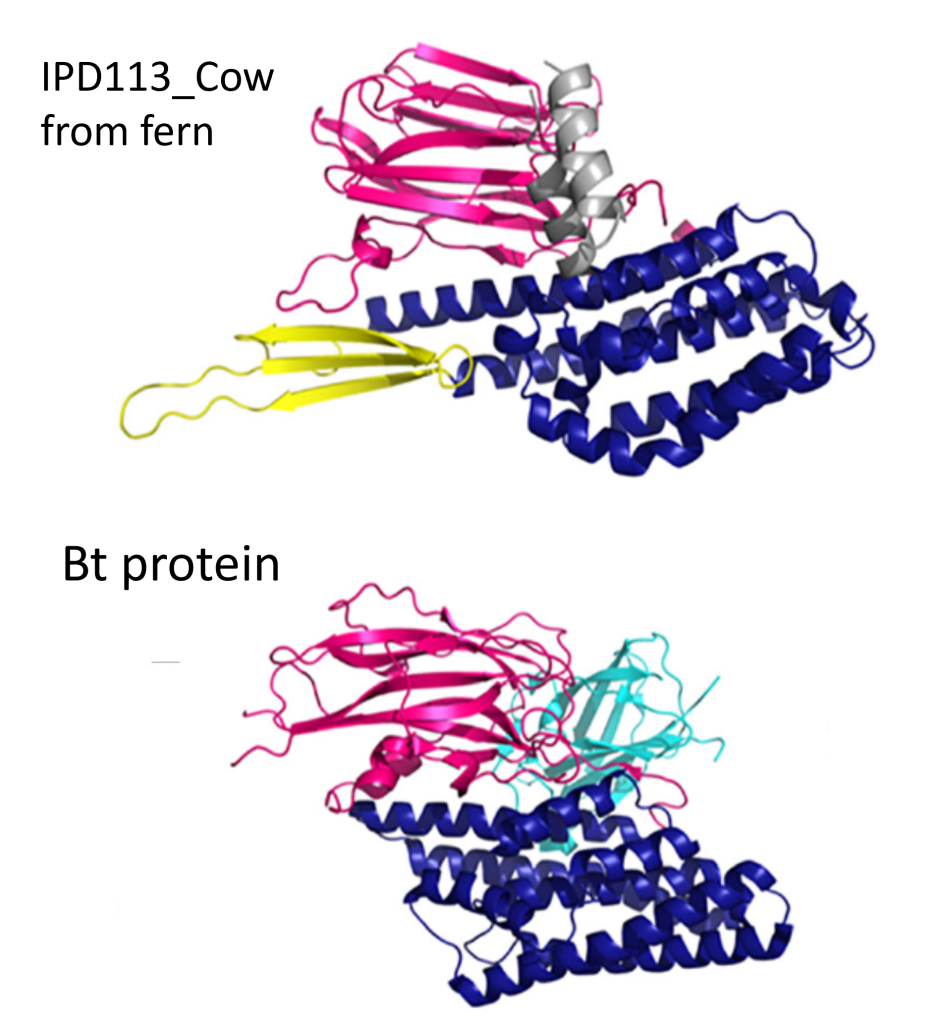
Ferns unleashed: Novel insecticidal proteins IPD113 challenge Bt resistance
Insect pests pose a significant threat to global crop production, with lepidopteran species like corn earworm and armyworms causing substantial losses. The widespread use of insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) in crops has been a key strategy to combat these pests. However, the emergence…

