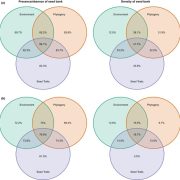
Machine learning algorithms predict soil seed bank persistence from easily available traits (Appl. Veg. Sci.)
Knowing whether a given plant species forms a persistent soil seed bank is essential to understanding its ecological dynamics, yet soil seed bank studies are both labor-intensive and time-consuming. One could argue that models should help predict this. Still, seed persistence in the soil is shaped by…
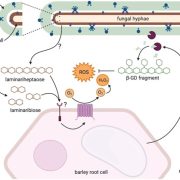
Fungal exopolysaccharide regulates plant-microbe interaction (Plant Cell)
The studies on the apoplastic interactions of plants and fungi often focus on the fungal cell-wall, but recent studies indicate various plant colonizing fungi also have an exopolysaccharide (EPS) layer outside their cell wall. Chandrasekar et al. observed that the composition of this fungal EPS is distinct…
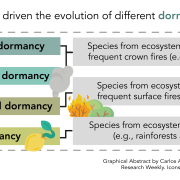
Review: Fire-released seed dormancy - a global synthesis (Biol. Rev)
In 1991, Jon E. Keely wrote the first review about the role of fire as a dormancy-breaking cue in California's Mediterranean ecosystems. In this review, almost 30 years after Keely's work, Pausas and Lamont provide us with an updated and worldwide vision of the subject. Four dormancy syndromes and their…
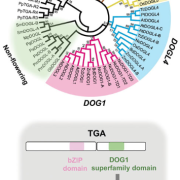
Opinion. Seed traits and phylogenomics: prospects for the 21st century ($) (Seed Sci)
In August 2021, The International Seed Science Society hosted its 13th International Conference. The meeting had many exciting presentations, including the keynote lecture given by Dr. Hiroyuki Nonogaki, entitled “Seed traits and pylogenomics: perspectives for the 21st Century”. This paper synthesizes…
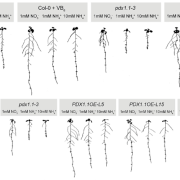
PDX1.1-dependent vitamin B6 synthesis alleviates ammonium toxicity-associated ROS production (Mol Plant)
Ammonium is a nitrogen form preferred by many plant species. However, high ammonium concentrations lead to decreased primary root elongation due to membrane depolarization and lower apoplastic pH. Liu et al. report that ammonium toxicity results in iron-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) production…
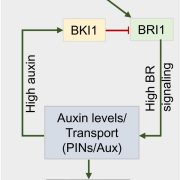
Nitrogen form dependent root foraging is regulated by auxin and brassinosteroid signaling (Plant Physiol.)
Root growth is highly sensitive to nitrogen (N), and affected by both the form and distribution of N. The hormone auxin is a major player in root growth response to N heterogeneity. Devi et al. report on the intricate interplay of auxin and brassinosteroid (BR) signaling in determining the root growth…

ROS homeostasis mediated by MPK4 and SUMM2 determines synergid cell death (Nature Comms)
Female gametophytes (FG) of angiosperms contain eight nuclei and seven cells, distributed in a defined manner. In the micropylar end of the FG there are two synergid cells and the haploid egg, while in the central cell there are two polar nuclei. The synergid cells are responsible for attracting the…

Bacterial avirulence gene encodes for a secreted protease and restricts host range (Mol Plant Path)
Plant pathogenic bacteria of the genus Clavibacter tend to have a narrow host range, but different species affect many important crops. Clavibacter michiganensis (Cm) causes bacterial wilt and canker in tomato, pepper and a few varieties of eggplant. There are no Cm-resistant tomato varieties but many…
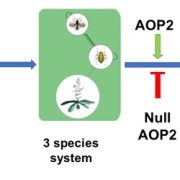
A plant gene that shapes its ecosystem (Science)
Keystone species shape the structure of an entire ecosystem, but can a gene determine structure of the whole ecosystem? A recent study indicates yes, some genes can, and such genes are called keystone genes. Barbour et al. set up a small ecosystem containing two herbivore aphids, one predator of these…

